Machine Learning Strategies for Preoperative PJI Diagnosis: Integrative Analysis of Serum and Synovial Fluid Markers
- PMID: 40771896
- PMCID: PMC12326324
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S499903
Machine Learning Strategies for Preoperative PJI Diagnosis: Integrative Analysis of Serum and Synovial Fluid Markers
Abstract
Background: Preoperative diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is crucial for guiding treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes. This study aims to develop a new diagnostic model for the preoperative diagnosis of PJI based on serum and synovial fluid markers and further validate its effectiveness.
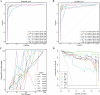
Methods: We retrospectively collected data from patients admitted for joint revision surgery between January 2018 and October 2022, selecting serum and synovial fluid markers as variables for the study. The most suitable diagnostic markers were selected using LASSO regression, and eight machine learning (ML) models were constructed based on the selected markers. The diagnostic performance and clinical utility of the ML models were assessed using receiver operating characteristic curves, calibration curves, decision curve analysis, and clinical impact analysis. Finally, the best model was compared to existing diagnostic standards using an external validation cohort.
Results: A total of 376 cases were analyzed (263 in the training cohort and 113 in the validation cohort), with 111 cases (29.52%) diagnosed as PJI. The ML models included SE-IL6, SE-CRP, ESR, SF-IL6, PMN%, DD, and ALB. The eXtreme Gradient Boosting model was the optimal model, achieving an area under the curve of 0.998 (95% CI 0.993-1) in the test set, outperforming other models. It also recorded the lowest Brier score of 0.062 and the highest F1 score of 0.985. In the external validation cohort, the accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of the ML diagnostic model were higher than those of the MSIS 2013 and ICM 2018 diagnostic criteria.
Conclusion: Our newly developed ML diagnostic model can assist clinicians in rapidly and accurately diagnosing PJI before surgery and has potential value for timing decisions regarding two-stage revisions. It has high economic value and clinical applicability.
Keywords: diagnostic model; inflammatory markers; machine learning; periprosthetic joint infection; preoperative diagnosis; synovial fluid.
© 2025 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

