VOPP1 as a Novel Susceptibility Gene in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Insights Into Its Mechanisms From Mendelian Randomization and Experimental Validation
- PMID: 40771899
- PMCID: PMC12327419
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S519727
VOPP1 as a Novel Susceptibility Gene in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Insights Into Its Mechanisms From Mendelian Randomization and Experimental Validation
Abstract
Background: Genetic factors are key determinants of vulnerability to rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a systemic inflammatory disease that causes inflammation, pain, swelling, and destruction of the joints. Expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) have been shown to detect novel disease-risk loci in previous studies. In this paper, we identified new susceptibility genes in RA and investigated their underlying mechanisms using integrated Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis.
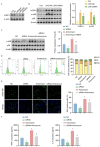
Methods: Two-sample MR analyses were used to determine the causative links among eQTLs, metabolites, and RA risk. The study was conducted between January 2023 and June 2024. Synovial tissue samples were collected from patients undergoing joint surgery at the Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University. Functional validation of the candidate gene vesicular overexpressed in cancer pro-survival protein 1 (VOPP1) was performed in vitro using rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes (RA-FLSs), and in vivo in a collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) rat model. Expression levels of VOPP1 were evaluated by quantitative real-time PCR and Western blot. Additional assays assessed cell proliferation, inflammatory cytokine expression, and activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway.
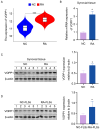
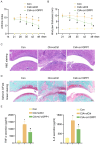
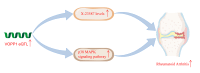
Results: Our findings offer the first evidence that RA risk is increased by the VOPP1 eQTL. Furthermore, we discovered that the VOPP1 eQTL positively modulates the X-23,587 metabolite's levels, and raising this metabolite may make RA risk worse. Moreover, we demonstrate that VOPP1 is highly expressed in RA synovial tissues and RA-FLSs. VOPP1 stimulates the proliferation of RA-FLSs and the inflammatory response through the p38 MAPK signaling pathway according to functional experiments. We showed that VOPP1 knockdown reduced articular damage and synovial inflammation in vivo using a CIA rat model.
Conclusion: This study identifies VOPP1 as a novel gene associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. VOPP1 may contribute to disease progression by elevating X-23,587 metabolite levels and activating the p38 MAPK signaling pathway.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; VOPP1; expression quantitative trait loci; fibroblast-like synoviocytes; p38 MAPK signaling pathway; rheumatoid arthritis; vesicular overexpressed in cancer pro-survival protein 1.
© 2025 Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification and validation of CKAP2 as a novel biomarker in the development and progression of rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 25;16:1606201. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1606201. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40636121 Free PMC article.
-
DS-Modified Paeoniflorin pH-Responsive Lipid-Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles for Targeted Macrophage Polarization in a Rat Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jul 12;20:8967-8992. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S516434. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40671689 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and synergistic effects of the active components of Xanthocerais lignum in inhibiting rheumatoid arthritis through the modulation of the biological behavior of synovial cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Aug 29;352:120200. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120200. Epub 2025 Jun 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40571227
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

