Harnessing nanotechnology for stem-cell therapies: revolutionizing neurodegenerative disorder treatments - a state-of-the-art update
- PMID: 40771915
- PMCID: PMC12325240
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1630475
Harnessing nanotechnology for stem-cell therapies: revolutionizing neurodegenerative disorder treatments - a state-of-the-art update
Abstract
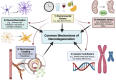
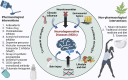
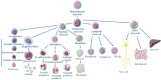
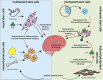
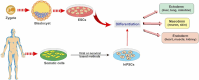
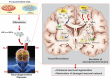
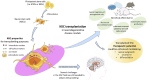
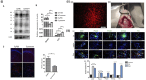
Neurodegenerative disorders, marked by the gradual degeneration and dysfunction of neurons, pose substantial clinical challenges due to the paucity of effective therapeutic strategies and the intricate and multifactorial nature of their underlying pathophysiology. On the other hand nanotechnology, Recent advancements in nanotechnology-driven interventions have significantly augmented the therapeutic potential of stem-cell therapies for the treatment of these complex conditions. Critical limitations in current therapeutic approaches have been highlighted, while potential future directions for their therapy have been outlined. Stem cell types-embryonic, induced pluripotent, and adult neural stem cells-are categorized, with a focus on their unique biological properties and therapeutic potentials in addressing neurodegenerative conditions. The role of nanomaterials in augmenting stem cell generation, scaffold fabrication, and targeted delivery mechanisms is examined, with particular emphasis on the capacity of nanotechnology to enhance regenerative processes and neuroprotective interventions. Nanomaterial-conjugated stem cell therapies are specifically addressed, focusing on their applications in neuronal recovery and treatment monitoring. Challenges associated with stem cell therapies, including ethical considerations, immunogenicity, and the necessity for stringent clinical validation, are critically examined. The integration of nanomedicine with stem cell research is proposed as a promising strategy to overcome these challenges and facilitate the development of novel therapeutic approaches. A comprehensive framework for future research is proposed, focusing on the synergistic integration of nanotechnological advancements with stem cell therapies to improve clinical outcomes and drive innovation in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. By integrating existing knowledge and highlighting critical gaps, this review seeks to foster continued research and interdisciplinary collaboration, accelerating progress in this rapidly evolving field.
Keywords: nanomaterial-conjugated regenerative therapy; nanomedicine; nanotechnology; neurodegenerative disorders; neuroprotective-nanotechnology stem-cell therapy; scaffold.
Copyright © 2025 Chengebroyen, Seelan, Yoonus Thajudeen, Alshehri, Biswas, Adur, Sundararajan, Lulu Sudhakaran and Singh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Emerging nanoparticle-based strategies to provide therapeutic benefits for stroke.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Jun 19. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-01492. Online ahead of print. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 40536921
-
The use of Open Dialogue in Trauma Informed Care services for mental health consumers and their family networks: A scoping review.J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2024 Aug;31(4):681-698. doi: 10.1111/jpm.13023. Epub 2024 Jan 17. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38230967
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pediatric Diffuse High-Grade Gliomas: A Comprehensive Review Of Ad-vanced Methods Of Diagnosis And Treatment.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.2174/0115680096365252250618115641. Online ahead of print. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2025. PMID: 40598730
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

