Engaging Essential Patient Support Personnel in Research as Patient Partners: A Survey Study
- PMID: 40772043
- PMCID: PMC12325099
- DOI: 10.2147/RMHP.S512398
Engaging Essential Patient Support Personnel in Research as Patient Partners: A Survey Study
Abstract
Introduction: Patient engagement in research is a collaborative interaction between patients and researchers throughout the entire research process. Healthcare workers provide care for others, but are the patients themselves in areas of workplace safety and mental health. Essential patient support personnel working on the front line of healthcare are particularly vulnerable but have an underrepresented voice in the research conducted about their health and work.
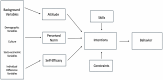
Methods: To explore this topic, a survey study of essential patient support personnel (N=42), guided by the Integrated Model of Behavioral Prediction, measured attitudes about engagement, behavioral intentions, and past engagement behavior. Skills and constraints, predictors of behavioral intentions for engagement in the model, were also assessed.
Results: Results showed that essential patient support personnel had positive attitudes and positive behavioral intentions to engage in research, yet only two participants had engaged in research in the past. Participants reported the most positive behavioral intentions to contribute at the preparation stage of research. Overwhelmingly, participants reported that the most important skill essential patient support personnel bring to a research team is their first-hand experience. Significant constraints to engagement included a lack of time, insufficient compensation, and job burnout.
Conclusion: Efforts to bolster patient engagement in research should focus on increasing the skills necessary for study execution (eg, study design and data analysis) and removing constraints to contribution (eg, providing appropriate monetary compensation, being mindful of time and heavy work schedules).
Keywords: healthcare workers; integrated model of behavioral prediction; patient centered outcomes research; patient engagement in research; survey research.
© 2025 Skubisz et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous