Assessing the effectiveness of the family health nurse model on self-management and glycated hemoglobin in middle-aged women with diabetes type 2: A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 40772079
- PMCID: PMC12327736
- DOI: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_35_24
Assessing the effectiveness of the family health nurse model on self-management and glycated hemoglobin in middle-aged women with diabetes type 2: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
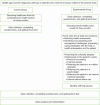
Background: Empowering patients with the skills and knowledge to manage their diabetes themselves, along with providing them with family support, are crucial factors that play a critical role in controlling diabetes. Given that nurses provide home visits to assist patients in the family health nurse model, this study aims to assess its effectiveness in improving self-management and glycated hemoglobin levels in middle-aged women with type 2 diabetes.
Methods and materials: The present clinical trial study, conducted in 2023, will be carried out on 84 middle-aged women who have been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes and are under the care of comprehensive health centers in Isfahan. They will be randomly assigned into two groups: intervention and control groups. Data will be collected using the Schmitt diabetes self-management questionnaire and glycated hemoglobin A1c test. For the intervention group, home visits will be conducted to identify diabetes self-management issues. Moreover, the intervention based on the family health nurse model will be implemented in three stages: pre-intervention, intervention, and evaluation. Statistical analysis will also include the Independent T-test and the Mancova and Ancova tests.
Conclusion: The family health nurse model considers family as the cornerstone of healthcare, recognizing its crucial societal role. In addition, the family's emotional and psychological support improves the patient's problem-solving ability. Evaluating the effectiveness of this model could bring valuable insights for healthcare policymakers, guiding them in devising targeted and effective strategies.
Keywords: Diabetes type 2; family health nurse model; glycated hemoglobin; self-management.
Copyright: © 2025 Journal of Education and Health Promotion.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
A digital intervention to improve mental health and interpersonal resilience for young people who have experienced online sexual abuse: the i-Minds non-randomised feasibility clinical trial and nested qualitative study.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025 Jul;13(28):1-27. doi: 10.3310/THAL8732. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025. PMID: 40754856
-
Adapting Safety Plans for Autistic Adults with Involvement from the Autism Community.Autism Adulthood. 2025 May 28;7(3):293-302. doi: 10.1089/aut.2023.0124. eCollection 2025 Jun. Autism Adulthood. 2025. PMID: 40539213
-
Survivor, family and professional experiences of psychosocial interventions for sexual abuse and violence: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Oct 4;10(10):CD013648. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013648.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36194890 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions to improve safe and effective medicines use by consumers: an overview of systematic reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 29;2014(4):CD007768. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007768.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24777444 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - PubMed
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas 2021. Available from: https://diabetesatlas.org/atlas/tenth-edition/
-
- Heidari K, Ahmadian M, Hosseinkhani R, Ravankhah Z, Taherian Z, Amini Z. Results of non-communicable diseases prevention and control program in Isfahan province. Scientific Journal of Kurdistan University of Medical Sciences. 2021;26:1–12. doi: 10.52547/sjku.26.5.1.
-
- Jokar M, Ghalavand A. The effect of twelve weeks of aerobic interval training on liver complications and cardiovascular risk factors in men with type 2 diabetes. Razi J Med Sci. 2022;29:26–36.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources