Exploring the oxidative and inflammatory markers landscape in Buerger's disease: A comparative analysis
- PMID: 40772104
- PMCID: PMC12327739
- DOI: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_146_24
Exploring the oxidative and inflammatory markers landscape in Buerger's disease: A comparative analysis
Abstract
Background: Buerger's disease (BD) is characterized by inflammation and blood clotting in smaller to medium-sized blood vessels of the extremities. This study aimed to explore oxidative stress and antioxidant capacity in BD compared to healthy smokers.
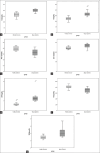
Materials and methods: A case-control study was conducted, involving 10 BD patients and 10 healthy smokers as controls, with average ages of 39.4 and 53.6 years, respectively. Various serum parameters, including total cholesterol (TCh), triglycerides (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (VLDL-C), antioxidant status (glutathione [GSH], antioxidant capacity [TAC], malondialdehyde [MDA]), and inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein [CRP], nitric oxide [NO]), were assessed.
Results: Circulating levels of total TAC (P = 0.01), TG (P < 0.01), TCh (P < 0.01), LDL (P = 0.028), MDA (P = 0.01), and CRP (P < 0.01) were significantly higher in BD patients compared to healthy smokers. No significant differences were found in VLDL-C (P = 0.42), GSH (P = 0.1), and NO (P = 0.82) activity. Additionally, TAC and HDL-C (P = 0.016) were significantly lower in BD patients.
Conclusion: Overall, our study reveals notable serum distinctions between BD patients and healthy smokers. BD patients exhibit reduced antioxidant levels, increased oxidative stress, lower HDL levels, and elevated LDL, total cholesterol, and borderline high triglyceride levels.
Keywords: Antioxidants; C-reactive protein; cholesterol; glutathione; malondialdehyde; nitric oxide; oxidative stress; thromboangiitis obliterans; triglycerides.
Copyright: © 2025 Journal of Education and Health Promotion.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological treatment for Buerger's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 11;3(3):CD011033. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011033.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 4;5:CD011033. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011033.pub4. PMID: 26967103 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Pharmacological treatment for Buerger's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Feb 1;2:CD011033. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011033.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 11;3:CD011033. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011033.pub3. PMID: 26828199 Updated.
-
Effect of Buerger's disease on ocular microvascular structure.Clin Exp Optom. 2025 Jul;108(5):607-613. doi: 10.1080/08164622.2024.2388129. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Clin Exp Optom. 2025. PMID: 39134365
-
Effect of adding fenofibrate versus curcumin to glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025 Jun 6;26(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s40360-025-00950-y. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40481568 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Oxidative Stress in Psoriasis Vulgaris Patients: Analysis of Asymmetric Dimethylarginine, Malondialdehyde, and Glutathione Levels.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 May 23;61(6):967. doi: 10.3390/medicina61060967. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40572655 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Watanabe Y, Miyata T, Shigematsu K, Tanemoto K, Nakaoka Y, Harigai M. Current trends in epidemiology and clinical features of thromboangiitis obliterans in Japan-A nationwide survey using the medical support system database. Circ J. 2020;84:1786–96. - PubMed
-
- Buerger L. Landmark publication from the American Journal of the Medical Sciences, “Thrombo-angiitis obliterans: A study of the vascular lesions leading to presenile spontaneous gangrene”. 1908. Am J Med Sci. 2009;337:274–84. - PubMed
-
- Mills JL. Buerger’s disease in the 21st century: Diagnosis, clinical features, and therapy. Semin Vasc Surg. 2003;16:179–89. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous