Primary Cutaneous Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-Positive Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma With Synchronous Systemic T-cell Lymphoma: A Case Report
- PMID: 40772145
- PMCID: PMC12327441
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.87441
Primary Cutaneous Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-Positive Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma With Synchronous Systemic T-cell Lymphoma: A Case Report
Abstract
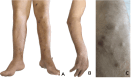
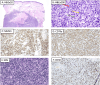
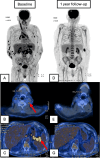
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a rare and aggressive lymphoma that has been associated with age-related immunosenescence. Here, we present the case of a 79-year-old man with violaceous nodules on the skin, mainly on the lower and upper limbs, diagnosed as primary cutaneous EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) based on histopathological and immunohistochemical findings. Systemic evaluation revealed synchronous peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified (NOS), without systemic B-cell lymphoma involvement. The patient was treated with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, hydroxydaunorubicin, vincristine (Oncovin), and prednisone (R-CHOP) chemotherapy, achieving a complete response for both lymphomas, with sustained outcomes after one year of follow-up. This case highlights the importance of age as a risk factor for EBV-related malignancies, the role of Epstein-Barr encoding region (EBER) and cluster of differentiation 30 (CD30) testing in diagnosis, and the potential effectiveness of R-CHOP in treating this rare lymphoma association. Further research is needed to establish optimal management strategies.
Keywords: case report; diffuse large b-cell lymphoma; ebv; r-chop; t-cell lymphoma.
Copyright © 2025, Soares et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Informed consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection in infancy. Chan KH, Tam JS, Peiris JS, Seto WH, Ng MH. J Clin Virol. 2001;21:57–62. - PubMed
-
- Age-related Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders: comparison with EBV-positive classic Hodgkin lymphoma in elderly patients. Asano N, Yamamoto K, Tamaru J, et al. Blood. 2009;113:2629–2636. - PubMed
-
- [Translated article] an update on EBV-related cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders: a systematic review. García-González S, Prieto-Torres L, García-García M. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2025;116:0–93. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
