Antiphospholipid Syndrome in a Patient With IgA Nephropathy: A Rare and Challenging Clinical Overlap
- PMID: 40772183
- PMCID: PMC12327936
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.87462
Antiphospholipid Syndrome in a Patient With IgA Nephropathy: A Rare and Challenging Clinical Overlap
Abstract
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is a rare autoimmune condition associated with a heightened risk of blood clots in arteries and veins due to the presence of specific antibodies. IgA nephropathy (IgAN), a kidney disorder involving immune complex deposition, is another immune-mediated disease. The coexistence of APS and IgAN is highly uncommon. We describe a young adult male with biopsy-confirmed kidney involvement who developed a significant clot in the lower limb. Despite appropriate treatment, the clot progressed, leading to complications in the lungs. Further investigation revealed laboratory findings consistent with APS. The patient underwent advanced interventions including clot removal and vascular procedures, followed by long-term treatment to prevent further clotting. This study emphasizes the clinical complexity when these two immune-mediated conditions overlap and underscores the importance of early detection and collaborative care in managing such rare and serious presentations.
Keywords: anticoagulation; antiphospholipid syndrome (aps); case report; deep venous thrombosis (dvt); iga nephropathy (igan); pulmonary embolism (pe); thrombectomy.
Copyright © 2025, Al-Anbagi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Informed consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Medical Research Center at Hamad Medical Corporation issued approval #MRC-04-25-704. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
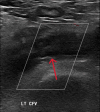
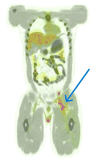


Similar articles
-
Home versus in-patient treatment for deep vein thrombosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 9;1(1):CD003076. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003076.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29315455 Free PMC article.
-
Stopping anticoagulation for isolated or incidental pulmonary embolism: the STOPAPE RCT protocol.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Jun;29(11):1-17. doi: 10.3310/HRCW7937. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 38970429 Free PMC article.
-
Antiplatelet and anticoagulant agents for secondary prevention of stroke and other thromboembolic events in people with antiphospholipid syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Oct 2;10(10):CD012169. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012169.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 12;10:CD012169. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012169.pub3. PMID: 28968483 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Antiplatelet agents for the treatment of deep venous thrombosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 25;7(7):CD012369. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012369.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35876829 Free PMC article.
-
Antiplatelet and anticoagulant agents for primary prevention of thrombosis in individuals with antiphospholipid antibodies.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 13;7(7):CD012534. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012534.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30004572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, et al. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4:295–306. - PubMed
-
- Diagnosis and management of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Garcia D, Erkan D. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:2010–2021. - PubMed
-
- Pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy. Barratt J, Feehally J, Smith AC. Semin Nephrol. 2004;24:197–217. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
