ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Despite Adequate Anticoagulation in a Patient With Triple-Positive Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Therapeutic Dilemma in a Resource-Limited Setting
- PMID: 40772199
- PMCID: PMC12327927
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.87433
ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Despite Adequate Anticoagulation in a Patient With Triple-Positive Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Therapeutic Dilemma in a Resource-Limited Setting
Abstract
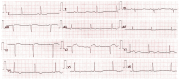
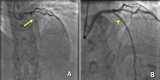
Antiphospholipid syndrome is a prothrombotic autoimmune disorder that can lead to arterial thrombotic events such as acute myocardial infarction. We report a case of a 40-year-old female with triple-positive antiphospholipid syndrome on therapeutic warfarin who presented with anterior ST-elevation myocardial infarction. With an international normalized ratio of 2.3, thrombolysis was contraindicated, and primary percutaneous coronary intervention was unavailable due to resource limitations. She was managed conservatively with enoxaparin, dual antiplatelet therapy, and supportive care. Elective angiography revealed complete occlusion of the left anterior descending artery, and viability testing guided subsequent percutaneous coronary intervention, resulting in good functional recovery. An individualized antithrombotic regimen with a clear timeline was offered after a multidisciplinary team discussion. This case highlights the therapeutic challenges of ST-elevation myocardial infarction in patients with anticoagulated antiphospholipid syndrome, particularly in settings without primary percutaneous coronary intervention.
Keywords: acute st myocardial infarction; anti-phospholipid antibodies; anti-phospholipid antibody syndrome (aps); percutaneous coronary intervention; primary pci; st-elevation myocardial infarction (stemi).
Copyright © 2025, Sivagurunathan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Informed consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An ST elevation myocardial infarction with multisystemic embolization: a shocking and striking first presentation of antiphospholipid syndrome: a case report.Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2025 Jun 24;9(7):ytaf296. doi: 10.1093/ehjcr/ytaf296. eCollection 2025 Jul. Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40697544 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing angiographic results of saline autotransfusion and thrombus aspiration in STEMI patients.Future Cardiol. 2025 Mar;21(4):237-243. doi: 10.1080/14796678.2025.2472581. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Future Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40035694
-
Antiplatelet and anticoagulant agents for primary prevention of thrombosis in individuals with antiphospholipid antibodies.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 13;7(7):CD012534. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012534.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30004572 Free PMC article.
-
Complete versus culprit-only revascularisation in ST elevation myocardial infarction with multi-vessel disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 3;5(5):CD011986. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011986.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28470696 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous recanalization following subtotal proximal LAD occlusion: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2025 Jul 3;19(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s13256-025-05369-x. J Med Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40611348 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, et al. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4:295–306. - PubMed
-
- Antiphospholipid syndrome and the risk of myocardial infarction: current evidence and uncertainties. Lóczi L, Kappelmayer J, Tarr T, Bagoly Z. Kardiol Pol. 2020;78:6–14. - PubMed
-
- Laboratory criteria for antiphospholipid syndrome: communication from the SSC of the ISTH. Devreese KM, Ortel TL, Pengo V, de Laat B. J Thromb Haemost. 2018;16:809–813. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
