Neural Networks for Semantic and Syntactic Prediction and Visual-Motor Statistical Learning in Adult Readers With and Without Dyslexia
- PMID: 40772236
- PMCID: PMC12328026
- DOI: 10.1162/nol.a.8
Neural Networks for Semantic and Syntactic Prediction and Visual-Motor Statistical Learning in Adult Readers With and Without Dyslexia
Abstract
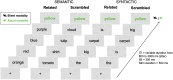
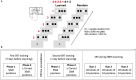
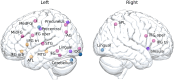
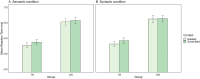
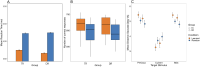
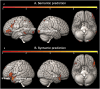
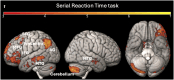
Prediction has become a key concept for understanding language comprehension, language production, and more recently reading. Recent studies suggest that predictive mechanisms in reading may be related to domain-general statistical learning (SL) abilities that support the extraction of regularities from sequential input. Both mechanisms have been discussed in relation to developmental dyslexia. Some suggest that SL is impaired in dyslexia with negative effects on the ability to make linguistic predictions. Others suggest that dyslexic readers rely to a greater extent on semantic and syntactic predictions to compensate for lower-level deficits. Here, we followed these two research questions in a single study. We therefore assessed the effects of semantic and syntactic prediction in reading and SL abilities in a population of university students with dyslexia and a group of typical readers using fMRI. The SL task was a serial reaction time (SRT) task that was performed inside and outside the scanner. The predictive reading task was performed in the scanner and used predictive versus nonpredictive semantic and syntactic contexts. Our results revealed distinct neural networks underlying semantic and syntactic predictions in reading, group differences in predictive processing in the left precentral gyrus and right anterior insula, and an association between predictive reading and SL, particularly in dyslexic readers. These findings contribute to our understanding of the interplay between SL, predictive processing, and compensation in dyslexia, providing new insights into the neural mechanisms that support reading.
Keywords: dyslexia; prediction; reading; semantics; sequence learning; syntax.
© 2025 Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Ashburner, J., Barnes, G., Chen, C.-C., Daunizeau, J., Flandin, G., Friston, K., Gitelman, D., Glauche, V., Henson, R., Hutton, C., Jafarian, A., Kiebel, S., Kilner, J., Litvak, V., Mattout, J., Moran, R., Penny, W., Phillips, C., Razi, A., … Zeidman, P. (2021). SPM12 manual. Wellcome Centre for Human Neuroimaging. https://www.fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk/spm/software/spm12/
-
- Bates, D., Mächler, M., Bolker, B., & Walker, S. (2015). Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67(1), 1–48. 10.18637/jss.v067.i01 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
