Cognitive impairment and p-tau217 are high in a vascular patient cohort
- PMID: 40772428
- PMCID: PMC12329572
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.70565
Cognitive impairment and p-tau217 are high in a vascular patient cohort
Abstract
Introduction: Vascular comorbidities are modifiable contributors to cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease (AD), yet brain health outcomes are rarely evaluated in cardiovascular patients.
Methods: This study prospectively evaluated cognition and AD pathology in 162 community-dwelling adults with asymptomatic cardiovascular disease who did not have a clinical diagnosis of dementia or cognitive impairment.
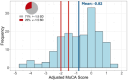
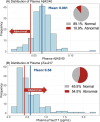
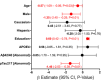
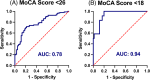
Results: Twenty-nine percent of the cohort had Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) scores indicative of cognitive impairment or dementia after adjusting for age, sex, and education based on National Alzheimer's Coordinating Center normative data. AD blood biomarker phosphorylated tau217 was elevated in 55% of the cohort, significantly associated with decreased MoCA scores (β = -1.46, 95% confidence interval [CI] -2.53 to -0.39, p < 0.01), and accurately differentiated cognitive impairment (area under the curve 0.94, 95% CI 0.88-0.99).
Discussion: This level of undiagnosed cognitive impairment and AD pathology exceeds what would be expected in the general population and highlights a potential need for screening and future work to better identify treatment options.
Highlights: Brain health outcomes are rarely evaluated in vascular patients. One hundred sixty-two adults with asymptomatic cardiovascular disease but without diagnoses of cognitive impairment or dementia were evaluated. Phosphorylated tau217 accurately differentiated cognitive impairment in patients with cardiovascular disease. High levels of cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease pathology are greatly underdiagnosed in the cardiovascular population.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; blood biomarkers; cognitive impairment; vascular disease; vascular risk factors.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
J.L.D. is an inventor on patents or patent applications of Eli Lilly and Company relating to the assays, methods, reagents, and/or compositions of matter for p‐tau assays and Aβ targeting therapeutics. J.L.D. has served as a consultant or on advisory boards for Eisai, Abbvie, Genotix Biotechnologies Inc., Gates Ventures, Gate Neurosciences, Dolby Family Ventures, Karuna Therapeutics, AlzPath Inc., Cognito Therapeutics, Inc., Prevail Therapeutics, and received research support from ADx Neurosciences, Fujirebio, AlzPath Inc., Roche Diagnostics, and Eli Lilly and Company in the past 2 years. J.L.D. has received speaker fees from Eli Lilly and Company and LabCorp. J.L.D. is a founder and advisor for Monument Biosciences. J.L.D. has stock or stock options in Eli Lilly and Company, Genotix Biotechnologies, AlzPath Inc., and Monument Biosciences. E.M.R. is a co‐founder and advisor of ALZpath, and a compensated scientific advisor to Alzheon, Denali, Cognition Therapeutics, Enigma, Retromer Therapeutics, and Vaxxinity. While the Quanterix ALZpath assay was used to characterize pTau217 levels, he was not involved in the analysis of data. None of the other authors declare that they have conflicts of interest. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01AG070987/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL159200/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Doris Duke Foundation
- University of Arizona Health Sciences Career Development Award
- Arizona Alzheimer's Consortium
- P30 AG072980/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG082930 Alzheimer Diagnosis in older Adults with Chronic Conditions ADACC Network
- CTR056039/Arizona Biomedical Research Commission
- CTR056056/Arizona Biomedical Research Commission
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Health Sciences, University of Arizona
- DDCF/Doris Duke Charitable Foundation/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

