Molecular and mechanical signatures contributing to mouse epidermal differentiation and barrier formation
- PMID: 40772711
- PMCID: PMC12331242
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.100961
Molecular and mechanical signatures contributing to mouse epidermal differentiation and barrier formation
Abstract
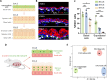
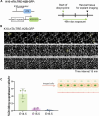
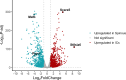
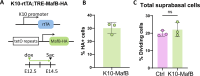
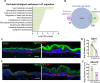
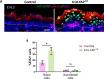
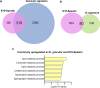
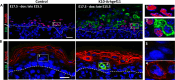
Formation of the skin barrier requires rapid proliferation coupled with differentiation and stratification of the embryonic epidermis. Basal progenitors give rise to progeny throughout development - first to intermediate cells, a transient proliferative suprabasal cell population, and later to spinous cells. Neither the function nor the differentiation trajectory of intermediate cells has been documented. We generated transcriptomes of intermediate and spinous cells and identified specific markers that distinguish these two populations. Further, we found that intermediate cells express a subset of genes in common with granular cells of the epidermis - the terminal living cell type that helps establish the barrier. Lineage tracing revealed that most intermediate cells directly transition to granular cells without expressing markers specific to spinous cells, thus revealing a distinct lineage pathway leading to granular fate. In addition to their transcriptional similarities, intermediate and granular cells both had hallmarks of increased actomyosin contractility. We found that rather than simply lying downstream of cell fate pathways, contractility was sufficient to suppress spinous fate and promote granular gene expression. Together, these data establish the molecular and mechanical characteristics of the developing epidermis that allow this tissue to rapidly develop barrier activity.
Keywords: contractility; development; developmental biology; epidermis; granular; interemediate cell; mouse.
© 2024, Prado-Mantilla et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AP, WN, TL No competing interests declared
Figures











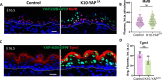
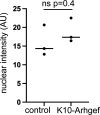
Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2024.07.23.604736
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.100961.1
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.100961.2
References
-
- Aleksander SA, Balhoff J, Carbon S, Cherry JM, Drabkin HJ, Ebert D, Feuermann M, Gaudet P, Harris NL, Hill DP, Lee R, Mi H, Moxon S, Mungall CJ, Muruganugan A, Mushayahama T, Sternberg PW, Thomas PD, Van Auken K, Ramsey J, Siegele DA, Chisholm RL, Fey P, Aspromonte MC, Nugnes MV, Quaglia F, Tosatto S, Giglio M, Nadendla S, Antonazzo G, Attrill H, Dos Santos G, Marygold S, Strelets V, Tabone CJ, Thurmond J, Zhou P, Ahmed SH, Asanitthong P, Luna Buitrago D, Erdol MN, Gage MC, Ali Kadhum M, Li KYC, Long M, Michalak A, Pesala A, Pritazahra A, Saverimuttu SCC, Su R, Thurlow KE, Lovering RC, Logie C, Oliferenko S, Blake J, Christie K, Corbani L, Dolan ME, Drabkin HJ, Hill DP, Ni L, Sitnikov D, Smith C, Cuzick A, Seager J, Cooper L, Elser J, Jaiswal P, Gupta P, Jaiswal P, Naithani S, Lera-Ramirez M, Rutherford K, Wood V, De Pons JL, Dwinell MR, Hayman GT, Kaldunski ML, Kwitek AE, Laulederkind SJF, Tutaj MA, Vedi M, Wang SJ, D’Eustachio P, Aimo L, Axelsen K, Bridge A, Hyka-Nouspikel N, Morgat A, Aleksander SA, Cherry JM, Engel SR, Karra K, Miyasato SR, Nash RS, Skrzypek MS, Weng S, Wong ED, Bakker E, Berardini TZ, Reiser L, Auchincloss A, Axelsen K, Argoud-Puy G, Blatter MC, Boutet E, Breuza L, Bridge A, Casals-Casas C, Coudert E, Estreicher A, Livia Famiglietti M, Feuermann M, Gos A, Gruaz-Gumowski N, Hulo C, Hyka-Nouspikel N, Jungo F, Le Mercier P, Lieberherr D, Masson P, Morgat A, Pedruzzi I, Pourcel L, Poux S, Rivoire C, Sundaram S, Bateman A, Bowler-Barnett E, Bye-A-Jee H, Denny P, Ignatchenko A, Ishtiaq R, Lock A, Lussi Y, Magrane M, Martin MJ, Orchard S, Raposo P, Speretta E, Tyagi N, Warner K, Zaru R, Diehl AD, Lee R, Chan J, Diamantakis S, Raciti D, Zarowiecki M, Fisher M, James-Zorn C, Ponferrada V, Zorn A, Ramachandran S, Ruzicka L, Westerfield M, Gene Ontology Consortium The gene ontology knowledgebase in 2023. Genetics. 2023;224:iyad031. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyad031. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aragona M, Sifrim A, Malfait M, Song Y, Van Herck J, Dekoninck S, Gargouri S, Lapouge G, Swedlund B, Dubois C, Baatsen P, Vints K, Han S, Tissir F, Voet T, Simons BD, Blanpain C. Mechanisms of stretch-mediated skin expansion at single-cell resolution. Nature. 2020;584:268–273. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2555-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G. Gene Ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nature Genetics. 2000;25:25–29. doi: 10.1038/75556. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

