Association of non-traditional lipid indices with diabetes and insulin resistance in US adults: mediating effects of HOMA-IR and evidence from a national cohort
- PMID: 40773099
- PMCID: PMC12331762
- DOI: 10.1007/s10238-025-01819-4
Association of non-traditional lipid indices with diabetes and insulin resistance in US adults: mediating effects of HOMA-IR and evidence from a national cohort
Abstract
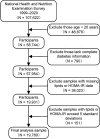
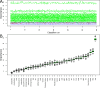
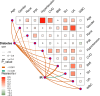
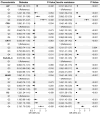
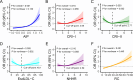
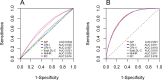
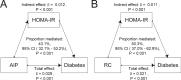
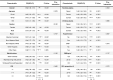
Dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, and insulin resistance (IR) are intricately linked. In recent years, a series of novel lipid indices have emerged. Investigating their correlation with diabetes and IR is critical for early intervention. This study analyzed 19,780 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) participants (1999-2020), examining the atherogenic index of plasma (AIP), Castelli risk index I (CRI-I) and II (CRI-II), estimated small dense LDL cholesterol (EsdLDL-C), non-HDL cholesterol-to-HDL cholesterol ratio (NHHR), and remnant cholesterol (RC). Covariates were selected via Boruta and LASSO regression. Multivariate logistic regression, restricted cubic splines, ROC, subgroup, and mediation analyses were employed, validated by sensitivity analyses. The prevalence of diabetes was 15.0%. After adjustment, four indices (excluding CRI-II and EsdLDL-C) were associated with diabetes. For Q4 vs Q1, AIP and RC showed significantly elevated risk (OR: 2.52 [2.07-3.07] and 2.13 [1.75-2.58], respectively). Regarding IR, all indices exhibited dose-dependent associations, with AIP (OR: 5.74 [5.00-6.59]) and RC (4.09 [3.58-4.67]) showing the strongest links. For diabetes diagnosis, AIP (AUC: 0.824) and RC (0.822) outperformed other lipid indices (cutoffs: 0.31, 31.0) but were less effective than fasting glucose and HbA1c. For IR, AIP (AUC: 0.837) and RC (0.830) remained superior among lipid indices and showed no significant diagnostic disadvantage vs IR-related indicators. Subgroup analyses indicated stronger AIP/RC-diabetes/IR associations in females. Mediation analyses showed HOMA-IR mediated 43.1% and 50.3% of AIP/RC-diabetes associations, more pronounced in older adults (> 65 years), males and those with BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2, while fatty acid intake did not affect these mediators. All six indices correlate with IR, but only AIP and RC strongly associate with diabetes, mediated by HOMA-IR. Females show enhanced AIP/RC-diabetes links, while older, male, and overweight groups exhibit greater HOMA-IR mediation. And AIP or RC's diagnostic performance for IR is not inferior to other IR assessment indices. Thus, AIP and RC are prioritized biomarkers for diabetes and IR monitoring.
Keywords: AIP; CRI-I; CRI-II; Diabetes; EsdLDL-C; HOMA-IR; NHHR; RC.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: The Ethics Review Board of the National Center for Health Statistics has undertaken a review and provided approval for the NHANES ethical policies to guarantee participants' voluntary informed consent. Consent for publication: Not applicable.
Figures
References
-
- Ferrari AJ, Santomauro DF, Aali A, Abate YH, Abbafati C, Abbastabar H, et al. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2021. Lancet. 2024;403:2133–61. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ginsberg HN, Huang L-S. The insulin resistance syndrome: impact on lipoprotein metabolism and atherothrombosis. Eur J Cardiovasc Risk. 2000;7:325–31. - PubMed
-
- Vergès B. Abnormal hepatic apolipoprotein B metabolism in type 2 diabetes. Atherosclerosis. 2010;211:353–60. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

