Transgenic augmentation of erythroferrone in mice ameliorates anemia in adenine-induced chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 40773297
- PMCID: PMC12487854
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.190018
Transgenic augmentation of erythroferrone in mice ameliorates anemia in adenine-induced chronic kidney disease
Abstract
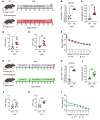
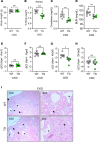
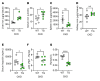
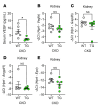
Anemia is a common and disabling complication of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Current therapies can be burdensome, and full correction of anemia is limited by their cardiovascular side effects. New approaches that may offer additional therapeutic options are needed. We explored the antianemic effects of erythroferrone, an erythroid hormone that induces iron mobilization by suppressing the master iron-regulatory hormone hepcidin. In a preclinical murine model of adenine-induced CKD, transgenic augmentation of erythroferrone mobilized iron, increased hemoglobin concentrations by approximately 2 g/dL, and modestly improved renal function without affecting systemic or renal inflammation, fibrosis, or markers of mineral metabolism. This study supports the concept that therapeutic augmentation of erythroferrone is a promising approach for alleviating CKD-associated anemia.
Keywords: Bone marrow differentiation; Chronic kidney disease; Hematology; Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Update of
-
Transgenic augmentation of erythroferrone in mice ameliorates anemia in adenine-induced chronic kidney disease.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 10:2024.12.06.627111. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.06.627111. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: JCI Insight. 2025 Aug 7;10(18):e190018. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.190018. PMID: 39713359 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- CDC. Chronic Kidney Disease in the United States, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/kidney-disease/php/data-research/index.html Accessed August 8, 2025.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

