Protocol for the induction of human spinal motor neurons from human induced pluripotent stem cells for studying amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- PMID: 40773352
- PMCID: PMC12348247
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2025.104016
Protocol for the induction of human spinal motor neurons from human induced pluripotent stem cells for studying amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Abstract
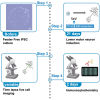
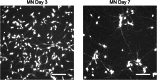
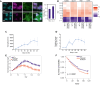
Here, we present a protocol for inducing spinal lower motor neurons (LMNs) from human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). We describe steps for preparation of a chemically induced transitional state (CTraS), transduction with Sendai virus, and LMN differentiation and maintenance. We then detail procedures for live imaging for single-cell-based survival analysis and neurite length of LMNs using BioStation and immunocytochemistry for induction efficiency check. This protocol is optimized for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) research and large-scale screening. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Setsu et al.1.
Keywords: Antibody; Cell Biology; Cell Differentiation; Cell culture; Cell-based Assays; Gene Expression; Microscopy; Molecular Biology; Neuroscience; Single Cell; Stem Cells.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests H.O. reports grants and personal fees from K Pharma, Inc., and SanBio Co., Ltd., outside the submitted work.
Figures


References
-
- Setsu S., Morimoto S., Nakamura S., Ozawa F., Utami K.H., Nishiyama A., Suzuki N., Aoki M., Takeshita Y., Tomari Y., Okano H. Swift induction of human spinal lower motor neurons and robust ALS cell screening via single-cell imaging. Stem Cell Rep. 2025;20 doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2024.11.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fujimori K., Matsumoto T., Kisa F., Hattori N., Okano H., Akamatsu W. Escape from Pluripotency via Inhibition of TGF-β/BMP and Activation of Wnt Signaling Accelerates Differentiation and Aging in hPSC Progeny Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2017;9:1675–1691. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.09.024. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

