Cost Effectiveness of the Reverse Sequence Algorithm Compared With the Traditional Algorithm for Syphilis Screening Among Pregnant Women
- PMID: 40773754
- PMCID: PMC12331245
- DOI: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000006019
Cost Effectiveness of the Reverse Sequence Algorithm Compared With the Traditional Algorithm for Syphilis Screening Among Pregnant Women
Abstract
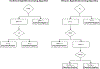
Objective: The traditional syphilis screening algorithm, which involves a nontreponemal assay followed by confirmatory treponemal testing, has been challenged by an alternative approach known as the reverse sequence algorithm. The latter reverses the order of the tests and incorporates a second treponemal test for discordant results. Although the reverse sequence may offer operational advantages, there is a need for formal cost-effectiveness analyses to compare these two syphilis screening alternatives.
Methods: We conducted cost-effectiveness analyses from the health care sector perspective to compare the reverse sequence with the traditional algorithm. We employed a decision tree for pregnant women in prenatal care that included the possibility of congenital syphilis outcomes. A simulated a cohort of 10,000 people was screened over 1 year to estimate total costs and quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) under each algorithm. We estimated incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs). Sensitivity analyses were performed to identify influential parameters affecting the ICERs and to conduct scenario analyses.
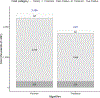
Results: During prenatal care, the reverse sequence detected four more cases, overtreated 185 more individuals, and prevented 0.42 more congenital syphilis cases (ICER $463,735/QALY gained), when compared with the traditional algorithm. Sensitivity analyses revealed that syphilis prevalence had the greatest effect on the ICER. To achieve ICERs below $50,000/QALY gained, syphilis prevalence would need to exceed 6% during prenatal care.
Conclusion: Our analysis indicates that, under likely parameter values, the reverse sequence algorithm is equally effective but more costly than the traditional algorithm and therefore not cost effective. Although treponemal test automation may offer potential savings in laboratory costs, these are outweighed by overtreatment costs.
Copyright © 2025 Written work prepared by employees of the Federal Government as part of their official duties is, under the U.S. Copyright Act, a “work of the United States Government” for which copyright protection under Title 17 of the United States Code is not available. As such, copyright does not extend to the contributions of employees of the Federal Government.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial Disclosure The authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Workowski KA, Berman S, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2010. MMWR Recomm Rep Morb Mortal Wkly Rep Recomm Rep. 2010;59(RR-12):1–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

