Multi-Center 3D CNN for Parkinson's disease diagnosis and prognosis using clinical and T1-weighted MRI data
- PMID: 40773786
- PMCID: PMC12351178
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2025.103859
Multi-Center 3D CNN for Parkinson's disease diagnosis and prognosis using clinical and T1-weighted MRI data
Abstract
Objective: Parkinson's disease (PD) presents challenges in early diagnosis and progression prediction. Recent advancements in machine learning, particularly convolutional-neural-networks (CNNs), show promise in enhancing diagnostic accuracy and prognostic capabilities using neuroimaging data. The aims of this study were: (i) develop a 3D-CNN based on MRI to distinguish controls and PD patients and (ii) employ CNN to predict the progression of PD.
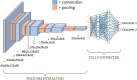
Methods: Three cohorts were selected: 86 mild, 62 moderate-to-severe PD patients, and 60 controls; 14 mild-PD patients and 14 controls from Parkinson's Progression Markers Initiative database, and 38 de novo mild-PD patients and 38 controls. All participants underwent MRI scans and clinical evaluation at baseline and over 2-years. PD subjects were classified in two clusters of different progression using k-means clustering based on baseline and follow-up UDPRS-III scores. A 3D-CNN was built and tested on PD patients and controls, with binary classifications: controls vs moderate-to-severe PD, controls vs mild-PD, and two clusters of PD progression. The effect of transfer learning was also tested.
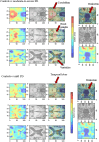
Results: CNN effectively differentiated moderate-to-severe PD from controls (74% accuracy) using MRI data alone. Transfer learning significantly improved performance in distinguishing mild-PD from controls (64% accuracy). For predicting disease progression, the model achieved over 70% accuracy by combining MRI and clinical data. Brain regions most influential in the CNN's decisions were visualized.
Conclusions: CNN, integrating multimodal data and transfer learning, provides encouraging results toward early-stage classification and progression monitoring in PD. Its explainability through activation maps offers potential for clinical application in early diagnosis and personalized monitoring.
Keywords: MRI; Machine learning; Parkinson’s disease.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Massimo Filippi reports financial support was provided by Ministry of Health. Silvia Basaia reports financial support was provided by Ministry of Health. Elisabetta Sarasso reports financial support was provided by Ministry of Health. Silvia Basaia reports a relationship with Ministero della Salute that includes: funding grants. Elisabetta Sarasso reports a relationship with Ministero della Salute that includes: funding grants. Federica Agosta reports a relationship with Biogen Idec, Italfarmaco, Roche, Zambon and Eli Lilly that includes: funding grants and speaking and lecture fees. Massimo Filippi reports a relationship with Alexion, Almirall, Bayer, Biogen, BMS, Celgene, Chiesi Italia, Eli Lilly, Genzyme, Janssen, Merck, Neopharmed Gentili, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Roche, Sanofi, Takeda, TEVA that includes: consulting or advisory, funding grants, and speaking and lecture fees. F. Agosta is Associate Editor of NeuroImage: Clinical; M. Filippi is Editor-in-Chief of the Journal of Neurology, Associate Editor of Human Brain Mapping, Neurological Sciences, and Radiology If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Balestrino R., Schapira A.H.V. Parkinson disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020;27:27–42. - PubMed
-
- Berg D., Borghammer P., Fereshtehnejad S.M., Heinzel S., Horsager J., Schaeffer E., Postuma R.B. Prodromal Parkinson disease subtypes - key to understanding heterogeneity. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021;17:349–361. - PubMed
-
- Braak H., Ghebremedhin E., Rüb U., Bratzke H., Del Tredici K. Stages in the development of Parkinson’s disease-related pathology. Cell Tissue Res. 2004;318:121–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

