Association between systemic immune-inflammation index and all-cause and CVD mortality in non-elderly diabetic adults
- PMID: 40774029
- PMCID: PMC12347989
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100739
Association between systemic immune-inflammation index and all-cause and CVD mortality in non-elderly diabetic adults
Abstract
Background: The Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) is widely studied for its role in evaluating Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) and mortality. However, its association with all-cause and CVD mortality in non-elderly diabetic adults remains unclear. This study aims to explore the relationship between SII and both all-cause and CVD mortality in non-elderly diabetic adults in the United States.
Methods: Cox proportional hazards models and subgroup analyses were used to assess the link between SII and mortality. Restricted Cubic Splines (RCS) examined the nonlinear association between SII and mortality.
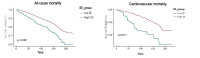
Results: Data from 4680 participants in NHANES (2001‒2018) were analyzed. Over an average follow-up of 98.3 months, there were 625 all-cause deaths and 162 CVD-related deaths. Participants were categorized into two SII groups (higher: > 947.625, lower: ≤ 947.625). Multivariable-adjusted models showed that higher SII levels were significantly associated with an increased risk of both CVD mortality (HR = 3.05; 95 % CI 1.85, 5.01) and all-cause mortality (HR = 1.97; 95 % CI 1.50, 2.58). Subgroup analyses confirmed the consistency of these associations. RCS analysis revealed a nonlinear relationship between SII and all-cause mortality, while the association with CVD mortality was linear.
Conclusion: Higher SII levels in non-elderly diabetic adults in the U.S. are linked to an increased risk of both CVD and all-cause mortality.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Diabetes; Mortality; Systemic immune-inflammation index.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier España, S.L.U.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ong K.L., Stafford L.K., McLaughlin S.A., Boyko E.J., Vollset S.E., Smith A.E., et al. Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2021. Lancet. 2023;402(10397):203–234. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Misra S., Ke C., Srinivasan S., Goyal A., Nyriyenda M.J., Florez J.C., et al. Current insights and emerging trends in early-onset type 2 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023;11(10):768–782. - PubMed
-
- Hu B., Yang X.R., Xu Y., Sun Y.F., Sun C., Guo W., et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(23):6212–6222. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources