Exome analysis links kidney malformations to developmental disorders and reveals causal genes
- PMID: 40774958
- PMCID: PMC12332173
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62319-3
Exome analysis links kidney malformations to developmental disorders and reveals causal genes
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Exome analysis links kidney malformations to developmental disorders and reveals causal genes.Nat Commun. 2025 Oct 9;16(1):8980. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-64910-0. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 41068109 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
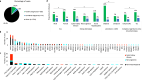
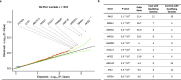
Congenital anomalies of the kidneys and urinary tract (CAKUT) are developmental disorders that commonly cause pediatric chronic kidney disease and mortality. We examine here rare coding variants in 248 CAKUT trios and 1742 singleton CAKUT cases and compare them to 22,258 controls. Diagnostic and candidate diagnostic variants are detected in 14.1% of cases. We find a significant enrichment of rare damaging variants in constrained genes expressed during kidney development and in genes associated with other developmental disorders, suggesting phenotype expansion. Consistent with these data, 18% of CAKUT patients with diagnostic variants have neurodevelopmental or cardiac phenotypes. We identify 40 candidate genes, including CELSR1, SSBP2, XPO1, NR6A1, and ARID3A. Two are confirmed as CAKUT genes: ARID3A and NR6A1. This study suggests that many yet-unidentified syndromes would be discoverable with larger cohorts and cross-phenotype analysis, leading to clarification of the genetic and phenotypic spectrum of developmental disorders.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: A.G.G. has served on advisory boards for Natera through a service agreement with Columbia University. A.G.G. has served on advisory boards for Actio Biosciences, Novartis, Vera, Vertex, and Travere. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Congenital Heart Defects (CHDs). https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/heartdefects/data.html (2024).
-
- World Health Organization. Congenital Disordershttps://www.who.int/health-topics/congenital-anomalies#tab=tab_1 (2025).
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- P20 DK116191/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K25 DK128563/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG007232/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG054023/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 5U54DK104309-10/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- U19 AI067854/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5K01DK132495/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01 AG037212/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 1S10OD030363-01A1/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R01 DK115574/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI100645/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01DK080099-13/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- K01 DK132495/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK138164/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 DK104309/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK080099/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- S10 OD030363/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK103184/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001873/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

