DNA vaccine targeting betacoronavirus spike protein blocks neuroinvasion and neuroinflammation in swine via dual antiviral-immunomodulatory action
- PMID: 40774966
- PMCID: PMC12331951
- DOI: 10.1038/s41541-025-01247-1
DNA vaccine targeting betacoronavirus spike protein blocks neuroinvasion and neuroinflammation in swine via dual antiviral-immunomodulatory action
Abstract
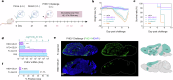
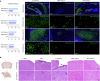
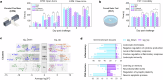
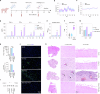
Porcine hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus (PHEV), a neurotropic betacoronavirus, causes fatal neurological disease in piglets, yet no licensed vaccines exist. Here, we developed a DNA vaccine encoding the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of PHEV spike protein fused to IgG1 Fc, adjuvanted with GEL01 (RBD + GEL01). Immunization in mice and piglets elicited robust neutralizing antibodies (titers up to 1:446 and 1:147, respectively) and Th1-biased cellular immunity. The vaccine restricted viral neuroinvasion, reducing brain viral loads by >90% and confining PHEV to discrete olfactory and cortical regions. Vaccinated animals exhibited preserved motor coordination, cognitive function, and minimal neuropathology. Transcriptomic analysis revealed suppression of proinflammatory mediators (e.g., Cxcl2, Saa3) and enhanced neural repair pathways, highlighting dual virological control and immunomodulatory mechanisms. As the first DNA vaccine against PHEV, the RBD + GEL01 candidate offers scalable protection against neurotropic coronaviruses by dual antiviral-immunomodulatory strategy, underscoring its potential to mitigate economic and zoonotic risks.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

