Urinary Complement proteome strongly linked to diabetic kidney disease progression
- PMID: 40775226
- PMCID: PMC12332033
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62101-5
Urinary Complement proteome strongly linked to diabetic kidney disease progression
Abstract
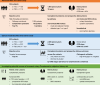
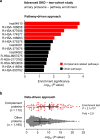
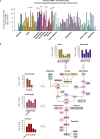
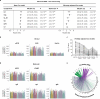
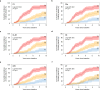
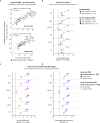
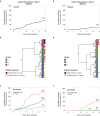
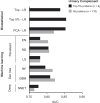
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) progression is not well understood. Using high-throughput proteomics, biostatistical, pathway and machine learning tools, we examine the urinary Complement proteome in two prospective cohorts with type 1 or 2 diabetes and advanced DKD followed for 1,804 person-years. The top 5% urinary proteins representing multiple components of the Complement system (C2, C5a, CL-K1, C6, CFH and C7) are robustly associated with 10-year kidney failure risk, independent of clinical covariates. We confirm the top proteins in three early-to-moderate DKD cohorts (2,982 person-years). Associations are especially pronounced in advanced kidney disease stages, similar between the two diabetes types and far stronger for urinary than circulating proteins. We also observe increased Complement protein and single cell/spatial RNA expressions in diabetic kidney tissue. Here, our study shows Complement engagement in DKD progression and lays the groundwork for developing biomarker-guided treatments.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: L.H.F. is an employee of and has an ownership interest in Fresenius Medical Care. M.A.N. has provided consulting to Otsuka, a member of the Educational Committee of the American Society of Nephrology and the Steering Committee of the Diabetic Foot Consortium. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Rios Burrows, N., Koyama, A. & Pavkov, M. E. Reported cases of end-stage kidney disease-United States, 2000-2019. Am. J. Transpl.22, 1483–1486 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Perkovic, V. et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med.380, 2295–2306 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Heerspink, H. J. L. et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med.383, 1436–1446 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01DK126799/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- P30DK036836 (to Joslin Diabetes Center)/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R61 DK131915/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30AG024824/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- UC4 DK101108/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK126799/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL67348 (PI Dr. Bowden)/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R01DK123459/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01DK041526/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01 DK071891/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5-CDA-2015-89-A-B/JDRF/United States
- R01NS075107/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- 17-2012-377/JDRF/United States
- P30 AG024824/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK087635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067348/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK036836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK105821/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R61DK131915/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01 DK123459/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK087635/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R34 DK097808/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK076007/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R34DK097808/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R03DK094484/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01DK071891/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01 NS075107/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK057521/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK041526/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK057521/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01DK076007/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- UC4DK101108/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- William Randolph Hearst Foundation Fellowship/Hearst Foundations (Hearst Foundation, Inc.)
- R01 DK105821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK094484/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

