Analysis of individual patient pathway coordination in a cross-species single-cell kidney atlas
- PMID: 40775269
- PMCID: PMC12415535
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-025-02285-0
Analysis of individual patient pathway coordination in a cross-species single-cell kidney atlas
Abstract
The use of single-cell RNA sequencing in clinical and translational research is limited by the challenge of identifying cell-type-specific, targetable molecular changes in individual patients and cross-species differences. Here we created an integrated single-cell kidney atlas including over 1 million cells from 140 samples, defining more than 70 conserved cell states in human and rodent models. We developed CellSpectra, a computational tool that quantifies changes in gene expression coordination across cellular functions, which we applied to kidney and lung cancer data. This tool powers our patient-level single-cell functional profiling report, which highlights cell-type-specific changes in the coordination of pathway gene expression in individuals. Our cross-species atlas facilitates the selection of a rodent model that closely reflects the cellular and pathway-level signatures observed in patient samples, advancing the application of single-cell methodologies in clinical precision medicine. Finally, using experimental models, we demonstrate how our informatics approach can be applied for the potential selection of suitable therapeutics.
© 2025. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The Susztak lab is supported by Gilead, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, GSK, BIPI, Regeneron, Genentech, ONO and Calico. K.S. is on the scientific advisory boards of Pfizer and Otsuka. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
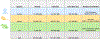
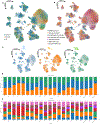

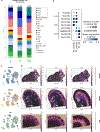












References
-
- Kidney disease: a global health priority. Nature Reviews Nephrology (2024).
-
- Kalantar-Zadeh K, Jafar TH, Nitsch D, Neuen BL & Perkovic V Chronic kidney disease. The Lancet 398, 786–802 (2021).
-
- Muntner P Longitudinal measurements of renal function. Seminars in nephrology 29, 650–657 (2009). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- Marietta-Blau Grant/Österreichische Agentur für Internationale Mobilität und Kooperation in Bildung, Wissenschaft und Forschung (Austrian Agency for International Cooperation in Education and Research)
- 5R01DK105821-08/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- 5R01DK132630-02/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- 5P50DK114786-07/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- 5R01DK087635-15/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R56 AG081351/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK087635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 2R01DK076077-15/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- Austrian Marshall Plan Foundation scholarship/Marshallplan-Jubiläumsstiftung (Austrian Marshall Plan Foundation)
- P50 DK114786/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK132630/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK076077/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- BA 6205/2-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- R01 DK105821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

