Multi-omics data reveal that SAA1 + fibroblasts exacerbate periodontitis by regulating macrophage inflammation and chemotaxis
- PMID: 40775345
- PMCID: PMC12330154
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-025-06925-1
Multi-omics data reveal that SAA1 + fibroblasts exacerbate periodontitis by regulating macrophage inflammation and chemotaxis
Abstract
Background: Traditional techniques are limited in their ability to analyze the complex interaction mechanisms among multiple cell types within the periodontal microenvironment, thereby restricting the development of targeted therapies for periodontitis (PD). Utilizing multiomics technologies to investigate the interaction networks of key cell clusters can systematically uncover regulatory mechanisms and identify critical therapeutic targets.
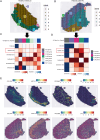
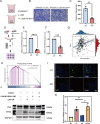
Methods: Through integrative analysis of single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), spatial transcriptomics, and bulk transcriptome datasets from periodontal tissues, we systematically characterized the spatial architecture and intercellular communication networks within the inflammatory periodontal microenvironment, identifying a functionally serum amyloid A1 + fibroblasts (SAA1 + Fib) that critically drives disease progression. Combined bioinformatics and functional validations (in vitro and in vivo) revealed the proinflammatory role of SAA1 + Fib, demonstrating their unique transcriptional profile and mechanistic contributions to periodontal inflammation.
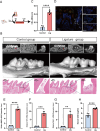
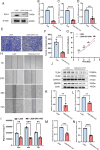
Results: This study successfully constructed a single-cell transcriptome atlas comprising 65,979 periodontal tissue cells and identified an SAA1 + fibroblast subpopulation with key functions. Cell communication analysis revealed that this subpopulation mediates the infiltration of myeloid cells, such as macrophages, to the lesion site by secreting chemokine-related signaling molecules, including members of the SAA, CXCL, and CSF families. Animal experiments confirmed a significant increase in SAA1 expression levels in both the gingival tissue and peripheral blood of periodontitis model mice. Gene function studies indicated that SAA1 knockout resulted in reduced migration ability and enhanced proliferation activity of L929 cells, while significantly decreasing the secretion of inflammatory factors such as IL-6 and TNF-α. In a co-culture system of L929 cells and RAW264.7 cells, SAA1 knockout not only diminished the chemotactic effect of fibroblasts on macrophages but also suppressed the secretion of inflammatory factors and inhibited M1 polarization of macrophages. Mechanistic studies indicated that these effects were likely mediated by the suppression of NF-κB signaling pathway activity in RAW264.7 cells.
Conclusion: We elucidated the pro-inflammatory properties of SAA1 + Fib and their role in promoting macrophage infiltration, targeting SAA1 offers a new approach for the treatment of PD.
Keywords: CellChat; Fibroblast; Macrophage infiltration; Periodontitis; SAA1; Single-cell RNA sequencing.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Interleukin (IL)-34 promotes the inflammatory role of IL-1β-producing myeloid cells in pemphigus lesions.Br J Dermatol. 2025 Jul 17;193(2):287-297. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljaf130. Br J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40203120
-
Integrated single-cell and transcriptomic analysis of bone marrow-derived metastatic neuroblastoma reveals molecular mechanisms of metabolic reprogramming.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 5;15(1):28519. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13626-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40764361 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell and spatial transcriptomics profile the interaction of SPP1+ macrophages and FAP+ fibroblasts in non-small cell lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025 Jul 31;14(7):2646-2669. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-2025-244. Epub 2025 Jul 25. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40799444 Free PMC article.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Adjunctive antimicrobial photodynamic therapy for treating periodontal and peri-implant diseases.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jul 12;7(7):CD011778. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011778.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38994711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kinane DF, et al. Periodontal diseases. Nat Reviews Disease Primers. 2017;3(17038). 10.1038/nrdp.2017.38. - PubMed
-
- Herrera D et al. Treatment of stage IV periodontitis: the EFP S3 level clinical practice guideline. J Clin Periodontology 2022 49 Suppl 24:4–71, 10.1111/jcpe.13639 - PubMed
-
- Teles F, et al. Viruses, periodontitis, and comorbidities. Periodontol 2000. 2022;89(1):190–206. 10.1111/prd.12435. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

