Troponin, NT-proBNP and postoperative atrial fibrillation in a prospective cohort undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery
- PMID: 40775411
- PMCID: PMC12331972
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-12122-3
Troponin, NT-proBNP and postoperative atrial fibrillation in a prospective cohort undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery
Abstract
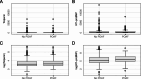
Troponin and N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) are biomarkers of cardiac damage and myocyte stretch. The existing evidence on the predictive value of preoperative high-sensitive Troponin and NT-proBNP concentration for the onset of postoperative atrial fibrillation (POAF) is inconsistent. Therefore, we aimed to assess these biomarkers as predictors for POAF in a prospective observational cohort study of patients without atrial fibrillation undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG). We analysed 423 patients with a median age of 66.3 years, 15.1% were women. About a third of these patients (N = 135, 32.4%) developed POAF. The median concentration of (25th, 75th percentile) high-sensitive Troponin at baseline was 11.8 (5.6, 42.7) ng/l in the POAF group and 11.4 (5.2, 37.0) ng/l in the group without POAF, median NT-proBNP was 255 (131, 621) ng/l in the POAF group and 184 (91, 497) in the group without POAF. In uni- and multivariable analyses neither biomarker showed statistically significant associations with POAF. These findings add further neutral data to the inconsistent results found in the current literature and mandate the search for better clinical or biomarker information to assess the risk of this common complication of CABG surgery.
Keywords: Biomarker; High-sensitive troponin I; High-sensitive troponin T; NT-proBNP; Postoperative atrial fibrillation; Risk prediction.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Eikelboom, R., Sanjanwala, R., Le, M-L., Yamashita, M. H. & Arora, R. C. Postoperative atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Thorac. Surg.111, 544–554 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Woldendorp, K., Farag, J., Khadra, S., Black, D., Robinson, B. & Bannon, P. Postoperative atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery: A meta-analysis. Ann. Thorac. Surg.112, 2084–2093 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Bianco, V., Kilic, A., Yousef, S. et al. The long-term impact of postoperative atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg.166, 1073–1083e10 (2023). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

