Pan-cancer landscape of ITGAV and its potential role in gastric cancer
- PMID: 40775431
- PMCID: PMC12332073
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-14342-z
Pan-cancer landscape of ITGAV and its potential role in gastric cancer
Abstract
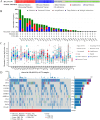
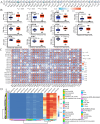
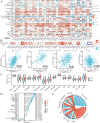
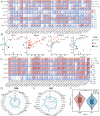
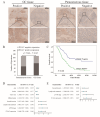
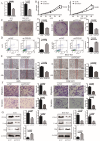
Integrin subunit alpha V (ITGAV), a subunit of the integrin receptor, is involved in many types of cancers. In order to explore the potential mechanisms of ITGAV in cancers, we carried out a comprehensive pan-cancer analysis using public database. In this study, ITGAV expression in different cancers and the relationship between ITGAV and clinic-pathological features, prognosis, genetic alteration, epigenetic modification, and tumor immune microenvironment were systemically analyzed. Gene enrichment analysis was performed to explore potential functions of ITGAV in gastric cancer (GC). GC tissue microarrays and in vitro cell experiments were used to verify the prediction results in GC. The results revealed that ITGAV was variably expression in different cancers, and ITGAV had a certain prognostic and diagnostic value in most cancers, including GC. ITGAV expression was found to be related to genetic alteration, DNA methylation, immune checkpoint gene, and immune cell infiltration in multiple cancers. Functional analyses revealed that ITGAV was involved in the regulation of EMC remodeling, ferroptosis, and cuproptosis in GC. In vitro experiments verified that ITGAV was correlated with GC cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion. Our study demonstrated that ITGAV can be used as an effective prognostic and immunological biomarker for multiple cancers. ITGAV can promote GC malignant progression and could serve as a potential therapeutic target for GC treatment.
Keywords: Bioinformatics analysis; Biomarker; Gastric cancer; ITGAV; Pan-cancer.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tianjin cancer hospital (No.bc2023054) and written informed consent was obtained from all patients. All methods in this study were performed in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and current ethical guidelines.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81401952/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- TJYXZDXK-009A/Tianjin Key Medical Discipline(Specialty) Construction Project
- TJYXZDXK-009A/Tianjin Key Medical Discipline(Specialty) Construction Project
- TJYXZDXK-009A/Tianjin Key Medical Discipline(Specialty) Construction Project
- TJYXZDXK-009A/Tianjin Key Medical Discipline(Specialty) Construction Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

