Arterial stiffness moderates the link between NfL and cognition: The IGNITE study
- PMID: 40775489
- PMCID: PMC12331445
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.70554
Arterial stiffness moderates the link between NfL and cognition: The IGNITE study
Abstract
Introduction: Arterial stiffness (carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity [cfPWV]) and plasma neurofilament light (NfL), markers of vascular and neuroaxonal aging, are linked to cognitive decline. Whether higher cfPWV amplifies the NfL-cognition relationship remains unclear.
Methods: Cognitively unimpaired older adults (N = 570) were assessed using composite cognitive scores from confirmatory factor analysis. cfPWV was dichotomized at the median. Plasma NfL was quantified on a Single Moleculte Array-High Definition, model X (SIMOA-HD X).
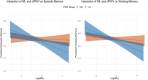
Results: Higher NfL correlated with poorer performance across all cognitive domains (p < 0.05), and higher cfPWV was linked to worse episodic memory, working memory, and processing speed (p < 0.05). NfL× cfPWV interactions were significant for episodic (β = 0.289, p = 0.048) and working memory (β = 0.287, p = 0.025), with stronger NfL-cognition associations in the higher cfPWV group (episodic memory: β = -0.324, p < 0.01; working memory: β = -0.343, p < 0.01).
Discussion: Greater cfPWV amplified the association between NfL-related axonal degeneration and cognitive decline.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT02875301 HIGHLIGHTS: Neurofilament light (NfL) and carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (cfPWV) each correlate with poorer cognitive function in older adults. Higher cfPWV exacerbates the link between NfL and cognitive deficits. Arterial stiffness may worsen NfL-related cognitive decline. Findings reveal synergy between vascular and neurodegenerative aging markers. Examining NfL or cfPWV alone may miss their synergistic effects on cognition.
Keywords: cardiorespiratory fitness; cognitive aging; episodic memory; neurofilament light; older adults; pulse wave velocity; vascular health; working memory.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
None for A.M.N., L.A.L., A.B.D., T.G.T., K.R.S., A.M.C., L.W., G.G., H.H., L.E.O., S.J., J.K.M., J.M.J., E.C., A.F.K., C.H.H., E.D.V., S.A.B., J.M.B., A.L.M., and C.K. T.K.K. has consulted/served on advisory board for Quanterix Corporation, SpearBio Inc., and Neurogen Biomarking LLC.; has stock equity interest in Neurogen Biomarking LLC.; and has received research support from Janssen Research Laboratories, outside the submitted work. He has received honoraria for speaker/grant review engagements from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), University of Pennsylvania (UPENN), University of Wisconsin‐Madison, AdventHealth, Brain Health conference, Barcelona‐Pittsburgh conference, the International Neuropsychological Society, the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, and Quebec Consortium for Drug Discovery (CQDM) Canada, all outside of the submitted work. T.K.K. has received blood biomarker data on defined research cohorts from Janssen and Alamar Biosciences for independent analysis and publication, with no financial incentive and/or research funding included. T.K.K. is an inventor on patents and provisional patents regarding biofluid biomarker methods, targets and reagents/compositions, and stands to benefit should his employer(s) transfer and/or licensing any of these resources to other organizations. K.I.E. is on the scientific advisory board for MedRhythms, Inc. and NeoAuvra, Inc. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- R01 AG075336/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG053952 to KIE/NIH/NIA
- K23 MH129882/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG072641/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R35 AG072307 to KIE/NIH/NIA
- P30 AG066468/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG073267/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DAF2255207/Aging Mind Foundation
- U01 NS131740/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HT94252320064/U.S. Department of Defense
- R35 AG072307/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR002366/Kansas University infrastructure grants
- Clinical and Translational Science Institute at the University of Pittsburgh
- R01 AG083874/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG023651/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG082930/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072973/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS141777/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH108509/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG023480/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG083156/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Professional Endowment from the Department of Psychiatry, University of Pittsburgh
- RF1 AG077474/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG025204/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025516/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002366/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG053952/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical