Pathway insights and predictive modeling for type 2 diabetes using polygenic risk scores
- PMID: 40775498
- PMCID: PMC12332094
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-13391-8
Pathway insights and predictive modeling for type 2 diabetes using polygenic risk scores
Abstract
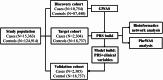
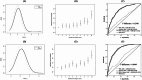
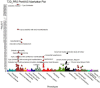
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) poses a significant global health burden. We developed a polygenic risk score (PRS) model based on genome-wide association study (GWAS) findings and integrated it with clinical data to predict T2D risk. This study analyzed electronic medical records from a major medical center in Taiwan, comprising 315,424 T2D cases and 141,484 controls. Fourteen genome-wide significant SNPs were identified and used to construct the T2D PRS. The integrated predictive model showed high accuracy (AUROC 0.842) and was validated in the Taiwan Biobank. A risk score ranging from 0 to 19 was established for clinical use. Phenome-wide association study (PheWAS) revealed links between PRSs and T2D-related complications, such as diabetic retinopathy and hypertension. Pathway analysis highlighted biological processes including IL-15 production and WNT/β-catenin signaling. Our findings support the use of PRSs in personalized T2D risk assessment and early prevention strategies.
Keywords: Pathway analysis; PheWAS; Polygenic risk score; Score system; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- The Ministry of Health and & Welfare, T. Statistics on causes of death in Taiwan in 2022 (2023). https://www.mohw.gov.tw/cp-16-74869-1.html.
-
- Cheng, C. F. et al. Genetic risk score constructed from common genetic variants is associated with cardiovascular disease risk in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Gene Med.23, e3305. 10.1002/jgm.3305 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

