Association between lncRNA H19 and osteoporosis in postmenopausal patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 40775721
- PMCID: PMC12330039
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-025-06153-9
Association between lncRNA H19 and osteoporosis in postmenopausal patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to assess the expression level of long non-coding RNA H19 (lncRNA H19) in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of postmenopausal patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) with comorbid osteoporosis (T2DM-OP), and to evaluate its diagnostic value and its role in the pathogenesis of T2DM-OP.
Methods: A total of 150 postmenopausal patients with T2DM were recruited from the First People's Hospital of Lianyungang City, China. Based on the bone mineral density (BMD) results measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), the patients were stratified into the T2DM-OP group (n = 108) and the T2DM group (n = 42). Clinical data and laboratory parameters were collected, and quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was used to quantitatively determine the expression of lncRNA H19 in PBMCs.
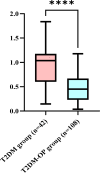
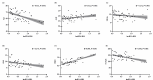
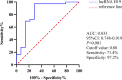
Results: When compared with the T2DM group, the expression level of lncRNA H19 in PBMCs of T2DM-OP patients was significantly lower (P < 0.001). The results of bivariate analysis revealed that lncRNA H19 was positively correlated with albumin (ALB, R = 0.311) and BMD (R = 0.696), while negatively correlated with age (R = -0.514), glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c, R = -0.272), fasting blood glucose (FBG, R = -0.275), and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1, R = -0.392). All of these correlations were statistically significant (R < 0.001). Binary logistic regression analysis identified age, body mass index (BMI), HbA1c, TGF-β1, and lncRNA H19 as independent risk factors for T2DM-OP. Additionally, multiple linear regression analysis demonstrated that age, HbA1c, FBG, TGF-β1, and BMD were key determinants of the expression of lncRNA H19. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis indicated that lncRNA H19 had high diagnostic accuracy for postmenopausal T2DM-OP, with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.833.
Conclusions: The expression level of lncRNA H19 in PBMCs of postmenopausal T2DM-OP patients was significantly reduced. This reduction could contribute to the pathogenesis of T2DM-OP through the regulation of modulating glucose metabolism and the lncRNA H19/TGF-β1 signaling pathway. Moreover, its expression level may serve as a highly promising non-invasive biomarker with high diagnostic accuracy for the early detection of postmenopausal T2DM-OP.
Trial registration: Retrospectively registered (ChiCTR2300074807).
Keywords: LncRNA H19; Osteoporosis; Peripheral blood mononuclear cells; Postmenopausal; TGF-β1; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Lianyungang First People’s Hospital (KY-20210712001-01) and registered with the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR2300074807). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiometabolic index is a novel predictor for osteoporosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with MAFLD: a cross-sectional study.Endokrynol Pol. 2025 Jul 29. doi: 10.5603/ep.105133. Online ahead of print. Endokrynol Pol. 2025. PMID: 40728427
-
The association between body roundness index and risk of osteoporosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study based on NHANES database.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2025 May-Aug;33(2):10225536251356804. doi: 10.1177/10225536251356804. Epub 2025 Jul 1. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2025. PMID: 40591954
-
Association between new anthropometric indices and osteoporosis in Chinese postmenopausal women- retrospective study based on hospitalized patients in China.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 May 16;16:1535540. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1535540. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40453580 Free PMC article.
-
Dipeptidyl-peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 analogues for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in people at increased risk for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 10;5(5):CD012204. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012204.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28489279 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and safety of vitamin D in relation to bone health.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007 Aug;(158):1-235. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007. PMID: 18088161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Farooqui KJ, Mithal A, Kerwen AK, Chandran M. Type 2 diabetes and bone fragility- an under-recognized association. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021;15(3):927–35. 10.1016/j.dsx.2021.04.017. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- YLZLXZ24G069/2024 Healthcare Quality (Evidence-Based) Management Research Project
- Lkxyb24160/2024 Lianyungang Association for Science and Technology Soft Science Research Project
- LYG06521202372/2023 Lianyungang Sixth Phase "521" Scientific Research Funding Project
- 202206/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- L202105/2021 Lianyungang Elderly health research project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

