Blood Pressure and Hypertension in Adolescents and Young Adults: Results From a Nationwide Screening Program
- PMID: 40776427
- PMCID: PMC12331881
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.70075
Blood Pressure and Hypertension in Adolescents and Young Adults: Results From a Nationwide Screening Program
Abstract
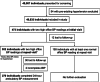
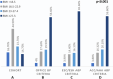
Literature on blood pressure (BP) norms in the adolescent and young adult (AYA) population remains sparse compared to adults. This study aims to describe the BP norms, prevalence of undiagnosed hypertension, and associations with demographic and anthropometric data among asymptomatic Asian AYA males. We studied retrospective cross-sectional data from individuals attending a national centralized BP screening program for enlistment over 30 months. Each individual's initial office BP reading was used to determine the cohort's BP norms. Individuals with a high reading, defined as systolic ≥140 mmHg and/or diastolic ≥90 mmHg, repeated office BP at a separate office visit. Those demonstrating two high readings underwent 24-h ambulatory BP (ABP) measurement. 49 033 males of median age 18.1 years were studied. The median, 75th centile, and 95th centile initial visit office BP readings were 121/74, 130/81, and 139/89 mmHg. 302 (0.62%; 95% CI, 0.55-0.69) were diagnosed with hypertension by office BP criteria. 270 underwent ABP measurement-180 (0.37%; 95% CI, 0.31-0.42) and 239 (0.49%; 95% CI, 0.43-0.55) had hypertension by ESC/ESH and ACC/AHA criteria, respectively. Higher weight, body mass index (BMI), and body fat percentage were associated with hypertension. The prevalence of undiagnosed hypertension among Asian AYA males is <1%. Norm-based cut-offs for high BP yielded absolute-value cut-offs similar to those recommended by adult guidelines; the 95th centile corresponded closely to 140/90 mmHg. Given similar diagnostic cut-offs with both norm-based and absolute-value approaches, both methods may be adopted. Focused screening of subgroups at higher risk of hypertension, such as obese individuals, may be considered in resource-limited settings.
Keywords: Asian; ambulatory blood pressure; epidemiology; screening.
© 2025 The Author(s). The Journal of Clinical Hypertension published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Higher blood pressure targets for hypertension in older adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 17;12(12):CD011575. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011575.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39688187
-
Pharmacotherapy for hyperuricemia in hypertensive patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jan 31;(1):CD008652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008652.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 13;4:CD008652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008652.pub3. PMID: 23440832 Updated.
-
Lifestyle Behaviors Among Adults Recommended for Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring According to the 2017 ACC/AHA Blood Pressure Guideline.Am J Hypertens. 2021 Nov 20;34(11):1181-1188. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpab110. Am J Hypertens. 2021. PMID: 34270687 Free PMC article.
-
Self-monitoring of blood pressure in hypertension: A systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis.PLoS Med. 2017 Sep 19;14(9):e1002389. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002389. eCollection 2017 Sep. PLoS Med. 2017. PMID: 28926573 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Isolated Diastolic Hypertension as Defined by the 2017 ACC/AHA Blood Pressure Guideline With Incident Cardiovascular Outcomes.JAMA. 2020 Jan 28;323(4):329-338. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.21402. JAMA. 2020. PMID: 31990314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bleyer W. A. and Albritton K., “Definition of Older Adolescent and Young Adult,” in Holland‐Frei Cancer Medicine, ed. Kufe D. W., Pollock R. E., Weichselbaum R. R., et al., 6th ed. (BC Decker, 2003), https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK13167/.
-
- Lurbe E., Agabiti‐Rosei E., Cruickshank J. K., et al., “2016 European Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents,” Journal of Hypertension 34, no. 10 (2016): 1887–1920. - PubMed
-
- Lee C. G., “The Emerging Epidemic of Hypertension in Asian Children and Adolescents,” Current Hypertension Reports 16, no. 12 (2014): 495. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

