The role of vitamin C on the skin
- PMID: 40776734
- PMCID: PMC12339815
- DOI: 10.4102/safp.v67i1.6098
The role of vitamin C on the skin
Abstract
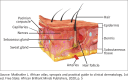
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid or ascorbate) plays an important role in regulating the health of the skin, promoting the differentiation of epithelial skin cells (keratinocytes) while contributing a notable role in the reduction of melanin synthesis, leading to antioxidative protection against solar-related skin damage. Vitamin C is only sourced from diet because humans have no ability to synthesise it in vivo. Routine dietary intake choices become key in maintaining the skin's integrity, preventing and treating some of the skin conditions encountered regularly by general practitioners and skin specialists alike. There is a strong association between vitamin C and the ageing process, skin pigmentation, control of certain skin diseases and a role in some skin cancers through antioxidation properties. Literature suggests that topical application of vitamin C in different forms of formulations has been demonstrated to have more clinical effect than oral intake.Contribution: This article spotlights the benefits of a vitamin commonly encountered in topical pharmaceutics, ingested as tablets or as part of our routine diet.
Keywords: UV radiation; ageing; antioxidant; ascorbic acid; diet; skin application; vitamin C; vitamin E.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that he has no financial or personal relationships that may have inappropriately influenced him in writing this article.
References
-
- Makhakhe L. African atlas, synopsis and practical guide to clinical dermatology. 1st ed. Free State: African Brilliant Minds Publishers, 2020; p. 5.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical