CREB regulates Foxp3+ST-2+ TREGS with enhanced IL-10 production
- PMID: 40777015
- PMCID: PMC12328323
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1601008
CREB regulates Foxp3+ST-2+ TREGS with enhanced IL-10 production
Abstract
Introduction: Regulatory T-cells (Tregs) are characterized by the expression of Foxp3, a master regulator involved in the development and function of Tregs. Foxp3 expression is dependent on activity of the Treg specific demethylated site (TSDR), which contains a CREB binding site. We aimed to find out how Foxp3 specific CREB deletion affects Treg expression and function.
Methods: Tregs from Foxp3creCREBfl/fl mice and wild type (CREBfl/fl ) mice were analyzed by flow cytometry. Cytokine analysis was performed by flow cytometry, ELISA and RT-qPCR. Gene expression analysis was performed using Affymetrix HTA2 assays, ATAC-sequencing, and Methylation-assays. For functional relevance, a CD4 T cell mediated transfer colitis was performed.
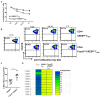
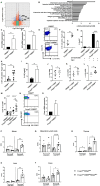
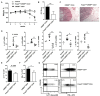
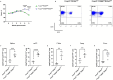
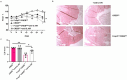
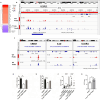
Results and discussion: Foxp3creCREBfl/fl mice showed increased frequencies of Tregs (CD25+/Foxp3+) in thymus, spleen and peripheral lymph nodes and in nonlymphoid organs including lung and colon, but decreased Foxp3 expression at the single cell level. Despite decreased Foxp3 expression, enhanced expression of the IL- 33 receptor (ST-2), IL-10, IL-13, and CREM was observed. CREB deficient Tregs were highly suppressive in vitro and prevented disease activity in a CD4 T cell mediated transfer colitis in an IL-10 dependent way. Mechanistically CREB fulfils dual roles in Tregs: (1) it promotes Foxp3 expression under Steady state conditions and (2) in cooperation with CREM, CREB restricts chromatin accessibility at the ST2 locus, thereby modulating IL-33 driven immune responses. This dual regulation balances FoxP3-dependent Treg stability with IL-10 mediated suppression of inflammation.
Keywords: CREB; CREM; Foxp3; IL-10; IL-33; ST2.
Copyright © 2025 Hebbar Subramanyam, Turyne Hriczko, Schulz, Look, Goodarzi, Clarner, Scheld, Kipp, Verjans, Böll, Neullens, Costa, Li, Gan, Denecke, Schippers, Floess, Huehn, Schmitt, Bopp, Wasmuth, Winograd, Beyaert, Lambrecht, Zenke, Wagner, Ohl and Tenbrock.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

References
-
- Zorn E, Nelson EA, Mohseni M, Porcheray F, Kim H, Litsa D, et al. IL-2 regulates FOXP3 expression in human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells through a STAT-dependent mechanism and induces the expansion of these cells in vivo . Blood. (2006) 108:1571–9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-02-004747, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

