Giant prostatic hyperplasia in a 54-years old patient treated by prostate artery embolization: case report
- PMID: 40777098
- PMCID: PMC12327336
- DOI: 10.3389/fruro.2024.1446650
Giant prostatic hyperplasia in a 54-years old patient treated by prostate artery embolization: case report
Abstract
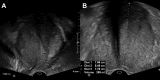
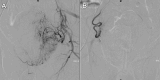
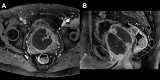
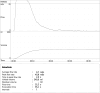
Giant prostatic hyperplasia (GPH) is defined as benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) of more than 200 ml. It is a challenging condition because transurethral resection is classically indicated for prostate volume less than 80 ml and open adenectomy remains the gold standard therapy for GPH. Herein, we present the case of a 54-years old male with giant prostatic hyperplasia (total prostate volume of 265 ml) causing lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and recurrent episodes of acute urinary retention. The patient refused the surgical adenomectomy and underwent bilateral prostate arteries embolization (PAE). Post embolization period was uneventful. Total prostate volume decreased progressively and LUTS disappeared. At more than 5 years follow-up the patient remains still asymptomatic, despite the discrete regrowth of the prostate detected on imaging. This case report suggests that PEA may be a good alternative to open surgery for patients with symptomatic GPH.
Keywords: endovascular procedures; interventional radiology; lower urinary tract symptoms; prostatic hyperplasia; therapeutic embolization; transurethral resection of prostate.
Copyright © 2024 Villard, Tsoumakidou, Moldovan, Rosset, Rouvière, Fassi-Fehri and Pagnoux.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wang MQ, Guo LP, Zhang GD, Yuan K, Li K, Duan F, et al. Prostatic arterial embolization for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms due to large (>80 mL) benign prostatic hyperplasia: results of midterm follow-up from Chinese population. BMC Urol. (2015) 15:33. doi: 10.1186/s12894-015-0026-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- EAU Guidelines . Edn. Presented at the EAU Annual Congress Paris April 2024. European Association of Urology; (2024) ISBN 978-94-92671-23-3. Available at: https://uroweb.org/guidelines/management-of-non-neurogenic-male-luts/cha....
-
- Zhang J, Wang Y, Li S, Jin S, Zhang S, Zhao C, et al. Efficacy and safety evaluation of transurethral resection of the prostate versus plasmakinetic enucleation of the prostate in the treatment of massive benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urol Int. (2021) 105:735–42. doi: 10.1159/000511116 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

