This is a preprint.
The CPEB ortholog Orb2 regulates brain size through the TRIM-NHL RNA-binding protein, Brain tumor
- PMID: 40777385
- PMCID: PMC12330577
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.07.18.665534
The CPEB ortholog Orb2 regulates brain size through the TRIM-NHL RNA-binding protein, Brain tumor
Abstract
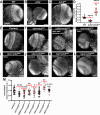
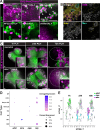
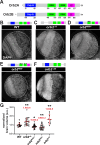
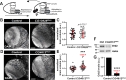
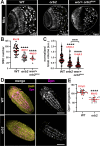
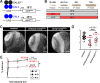
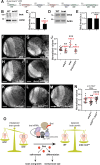
Neurodevelopment requires precise translational control, the disruption of which is implicated in various neurological disorders, including developmental delays, intellectual disability, and microcephaly. We report a novel role for the Drosophila CPEB-family protein Orb2, a translational regulator, in controlling brain size in a dose dependent manner. Loss of orb2 results in larval brain hypotrophy, whereas orb2 overexpression causes brain overgrowth. We demonstrate that orb2 is required for neural stem cell development from embryonic stages through larval neurogenesis. Structure-function analysis reveals that Orb2 RNA-binding activity promotes brain growth, while its poly-Q and ZZ domains act to restrain overgrowth. Further genetic and biochemical evidence indicates that orb2 functions upstream of the translational repressor Brain tumor (Brat), modulating Brat protein levels and, consequently, influencing brain size. These findings support a model wherein the antagonistic activities of Orb2 and Brat are critical for balanced brain growth during Drosophila neurodevelopment.
Keywords: brain growth; microcephaly; models of human disease; neurodevelopment; organ size.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures and competing interests The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Abdel-Salam G. M. H., Sayed I. S. M., Afifi H. H., Abdel-Ghafar S. F., Abouzaid M. R., Ismail S. I., Aglan M. S., Issa M. Y., El-Bassyouni H. T., El-Kamah G., Effat L. K., Eid M., Zaki M. S., Temtamy S. A., & Abdel-Hamid M. S. (2020). Microcephalic osteodysplastic primordial dwarfism type II: Additional nine patients with implications on phenotype and genotype correlation. Am J Med Genet A, 182(6), 1407–1420. 10.1002/ajmg.a.61585 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
