This is a preprint.
Environmental and Maternal Imprints on Infant Gut Metabolic Programming
- PMID: 40777448
- PMCID: PMC12330730
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.07.24.666662
Environmental and Maternal Imprints on Infant Gut Metabolic Programming
Abstract
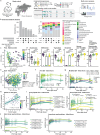
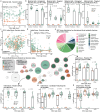
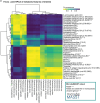
Early life is a critical period for immune and metabolic programming, but developmental patterns remain underexplored in populations from low- and middle-income countries. Here, we profiled the microbiome and metabolome of 55 Bangladeshi mother-infant dyads over the first six months of life. Importantly, we observed an increase in microbially-derived bile amidates and N-acyl lipids with age in conjunction with reads matching the bile salt hydrolase/transferase (bsh) gene. While microbial source tracking confirmed maternal fecal seeding, a substantial environmental contribution was also highlighted. Differences in infant fecal metabolic profiles were associated with delivery mode, maternal milk composition, household assets, and household-level water treatment. C-section delivery and untreated drinking water were linked to transient metabolic differences, including increases in bile amidates, N-acyl lipids, and other host-microbe co-metabolic products, including acylcarnitines. Multi-omics analysis revealed specific microbial-metabolite relationships, highlighting how early environmental and maternal living circumstances shape metabolic gut programming through the microbiome.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: P.C.D. is an advisor and holds equity in Cybele, Sirenas, and BileOmix, and he is a scientific co-founder, advisor, holds equity and/or receives income from Ometa, Enveda, and Arome with prior approval by UC San Diego. P.C.D. consulted for DSM Animal Health in 2023. R.K. is a scientific advisory board member, and consultant for BiomeSense, Inc., has equity and receives income. R.K. is a scientific advisory board member and has equity in GenCirq. R.K. is a consultant and scientific advisory board member for DayTwo, and receives income. R.K. has equity in and acts as a consultant for Cybele. R.K. is a co-founder of Biota, Inc., and has equity. R.K. is a co-founder and has equity and is a scientific advisory board member of Micronoma, and has equity. R.K. is a board member of Microbiota Vault, Inc. R.K. is a board member of N=1 IBS advisory board and receives income. R.K. is a Senior Visiting Fellow of HKUST Jockey Club Institute for Advanced Study. The terms of these arrangements have been reviewed and approved by the University of California San Diego in accordance with its conflict of interest policies. D.M. is a consultant for, and has equity in, BiomeSense, Inc. The terms of these arrangements have been reviewed and approved by the University of California, San Diego. L.B. is a co-inventor on patent applications related to the use of HMOs in preventing NEC and other inflammatory diseases. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Renz H., Brandtzaeg P. & Hornef M. The impact of perinatal immune development on mucosal homeostasis and chronic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 12, 9–23 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Bäckhed F. et al. Dynamics and stabilization of the human gut microbiome during the first year of life. Cell Host Microbe 17, 690–703 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
