High-dose-rate brachytherapy lowers travel burden for men with localized prostate cancer compared with external beam radiation
- PMID: 40777601
- PMCID: PMC12327330
- DOI: 10.3389/fruro.2025.1598726
High-dose-rate brachytherapy lowers travel burden for men with localized prostate cancer compared with external beam radiation
Abstract
Objective: There are many treatment options for localized prostate cancer, including external beam radiation therapy (EBRT), stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT), and prostate brachytherapy (BT). This study aimed to compare the travel burdens of high-dose-rate brachytherapy (HDR-BT) at our BT center and EBRT or SBRT if administered close to home.
Materials and methods: This single-institution retrospective cohort study included 69 patients who had HDR-BT monotherapy for their prostate cancer from August 2017 to December 2022. The travel burden for HDR-BT monotherapy was estimated using Google Maps by measuring the distance from each patient's home address to our BT center. The total travel burden was calculated by multiplying the number of treatment fractions required for each modality by the roundtrip travel distance between the home and the treatment facility. Treatment toxicity was evaluated using the Expanded Prostate Index Composite for Clinical Practice (EPIC-CP) questionnaire.
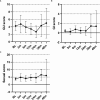
Results: The median age of the 69 patients was 67 years. The mean distance from home to the BT center was 37.4 mi, while the mean distance to the nearest radiation facility was 8.3 mi. The mean total travel distance for HDR-BT was 150 mi, while those for EBRT and SBRT were 463 and 83 mi, respectively. HDR-BT resulted in a mean travel burden reduction of 313 mi compared with EBRT. The EPIC-CP scores indicated minimal posttreatment toxicity, with most patients reporting stable or improved symptoms.
Conclusion: HDR-BT monotherapy significantly reduces the travel burden compared with EBRT for localized prostate cancer, with minimal treatment-associated toxicity. Increasing the availability of BT centers could further alleviate the travel burden. Alternatively, providing transportation support could improve access to care.
Keywords: access to care; external beam radiation therapy; high-dose-rate brachytherapy; patient travel burden; prostate cancer.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Yang, Bylund, Cummings and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for high-risk prostate cancer: Where are we now?Pract Radiat Oncol. 2018 May-Jun;8(3):185-202. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2017.11.008. Epub 2017 Dec 2. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29339046
-
A Systematic Review of the Efficacy and Toxicity of Brachytherapy Boost Combined with External Beam Radiotherapy for Nonmetastatic Prostate Cancer.Eur Urol Oncol. 2024 Aug;7(4):677-696. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2023.11.018. Epub 2023 Dec 26. Eur Urol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38151440
-
High-dose-rate (HDR) brachytherapy boost in combination with external beam radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer: An evidence-based consensus statement.Brachytherapy. 2025 Jul 23:S1538-4721(25)00117-5. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2025.06.005. Online ahead of print. Brachytherapy. 2025. PMID: 40707306
-
Dosimetric Comparison of VMAT Alone and VMAT with HDR Brachytherapy Boost Using Clinical and Biological Dose Models in Localized Prostate Cancer.Curr Oncol. 2025 Jun 19;32(6):360. doi: 10.3390/curroncol32060360. Curr Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40558303 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Brachytherapy With External Beam Radiation Therapy Versus Brachytherapy Alone for Intermediate-Risk Prostate Cancer: NRG Oncology RTOG 0232 Randomized Clinical Trial.J Clin Oncol. 2023 Aug 20;41(24):4035-4044. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.01856. Epub 2023 Jun 14. J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37315297 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Society AC. Key statistics for prostate cancer (2024). Available online at: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/prostate-cancer/about/key-statistics... (Accessed June 23, 2025).
-
- Slevin F, Zattoni F, Checcucci E, Cumberbatch MGK, Nacchia A, Cornford P, et al. A systematic review of the efficacy and toxicity of brachytherapy boost combined with external beam radiotherapy for nonmetastatic prostate cancer. Eur Urol Oncol. (2024) 7:677–96. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2023.11.018 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
