Trends in the prevalence of pediatric lower urinary tract symptoms in a national claims database of privately insured patients, 2007-2016
- PMID: 40777611
- PMCID: PMC12327348
- DOI: 10.3389/fruro.2025.1422897
Trends in the prevalence of pediatric lower urinary tract symptoms in a national claims database of privately insured patients, 2007-2016
Abstract
Background: Pediatric lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) impact a significant number of children and families worldwide. Estimated prevalences rely on small cross-sectional studies, leading to inconsistent estimates. This study aims to characterize demographic and temporal trends in LUTS prevalence within a national claims database of privately insured individuals in the United States.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study by reviewing the Merative™ MarketScan® Outpatient Research Database v2.0 between 2007-2016. Patients with neurogenic bladder, renal transplant, structural urologic disease, and concurrent urinary tract infection were excluded. Yearly trends were reviewed across age, sex, geographic region, and clinical comorbidities such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and constipation. Yearly frequency of diagnostic codes was calculated to characterize LUTS diagnostic coding practices.
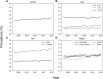
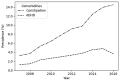
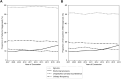
Results: We identified 1,625,538 patients aged 5-18 years with LUTS, representing 6% of the total population at risk, with a median age of 8.0 years. More patients in the cohort were female (66.1%), between 5-10 years old (57.9%), and resided in the Southern US (38.5%). The yearly prevalence of LUTS significantly increased from 1.8% to 2.1% yearly, and saw significant increases in females, 15-18 year old patients, and across several geographic regions. Comorbid constipation and ADHD within LUTS patients also significantly increased. Diagnostic coding practices remained stable.
Conclusions: Families of patients with LUTS are increasingly seeking medical care for their condition. These results exceed similar estimates from previous longitudinal studies and can inform population-level intervention strategies. Further studies should investigate the impact of LUTS on healthcare resource utilization, including in non-privately insured populations.
Keywords: administrative claims; healthcare; lower urinary tract symptoms; pediatrics; retrospective studies; urology.
Copyright © 2025 Brosula, Venkatapuram, Chen, Zhang and Kan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Vasconcelos Mm de A, Bastos JM, Arana IE, Teixeira IB, Lima EM, Carvalho TA, et al. Association between Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and lower urinary tract symptoms in children and adolescents in a community setting. Int Braz J Urol Off J Braz Soc Urol. (2021) 47:969–78. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2020.0978 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
