Follow-up study of vonoprazan maintenance therapy for reflux esophagitis: A 96-week evaluation in patients with PPI-refractory disease
- PMID: 40777627
- PMCID: PMC12329401
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2025.2038
Follow-up study of vonoprazan maintenance therapy for reflux esophagitis: A 96-week evaluation in patients with PPI-refractory disease
Abstract
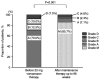
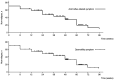
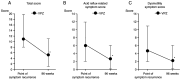
Vonoprazan is a potassium-competitive acid blocker that provides more potent and sustained acid suppression than conventional proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). Vonoprazan may serve a role in the long-term management of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), particularly in patients with reflux esophagitis (RE) who are unresponsive to PPIs. The present study aimed to evaluate the safety, tolerability and efficacy of vonoprazan over a 96-week period in patients with PPI-refractory RE. Initially, 74 patients received vonoprazan 20 mg once daily for 4 weeks. Patients who demonstrated mucosal healing transitioned to vonoprazan 10 mg once daily for a 48-week maintenance phase. Of these, 43 patients continued therapy for an additional 48 weeks. Endoscopic evaluation, symptom scores using the Frequency Scale for the Symptoms of GERD and serum gastrin levels were monitored to assess treatment outcomes and safety. By the end of the 96-week maintenance period, 85.7% of patients who completed follow-up showed no recurrence of mucosal lesions. Among those who discontinued therapy following symptom resolution, 45.8% experienced symptom relapse; however, these patients responded well to reintroduction of vonoprazan. Although serum gastrin levels in the continuous maintenance therapy remained elevated, no adverse events such as carcinoid tumors were reported. These findings suggested that vonoprazan was both effective and well-tolerated as a long-term maintenance therapy for RE and may serve as a viable on-demand treatment strategy for relapse management. While the results are promising, they stem from a highly selected population. Therefore, further randomized, controlled trials are warranted to confirm the generalizability and long-term safety of vonoprazan in broader GERD populations.
Keywords: gastroesophageal reflux disease; maintenance treatment; recurrent reflux esophagitis; vonoprazan.
Copyright: © 2025 Mizuno et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Alqassab DF, Hasan MJ, AlSaadoon AM, AlMuqahwi AJ, AlAwadhi FA, Bahram SA, Alsayyad AS. Prevalence and risk factors of gastroesophageal reflux disease among adults attending primary healthcare in Bahrain. J Family Med Prim Care. 2024;13:5758–5765. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_968_24. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
