Intracardiac Cement Embolism Following Vertebroplasty
- PMID: 40777721
- PMCID: PMC12331201
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.87535
Intracardiac Cement Embolism Following Vertebroplasty
Abstract
This case report presents a 70-year-old female patient who was diagnosed with an intracardiac cement embolism two months after a percutaneous vertebroplasty of her L4 vertebra. Although percutaneous vertebroplasty is generally considered a safe procedure, this case highlights the potential for serious complications. The patient was on oral vitamin K antagonist for the past 20 years for an unprovoked deep vein thrombosis and on statins for a chronic dyslipidemia. Although being mildly dyspneic after the operation, the patient presented to the emergency department after two months for a worsening dyspnea. Diagnostic imaging confirmed the presence of a large cement embolus fixed in the coronary sinus, associated with extensive tricuspid valve damage. An open-heart surgery for cement embolus removal and replacement of the valve was performed. This case underscores the importance of such complications for a rapid diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: cement extravasation; intracardiac cement embolism; multimodality cardiac imaging; right heart dysfunction; vertebroplasty complication.
Copyright © 2025, Hamade et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Informed consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
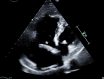

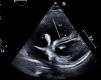
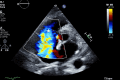
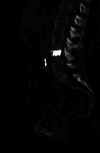


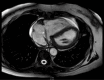

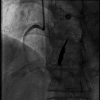
References
-
- Vertebral augmentation. Amans MR, Carter NS, Chandra RV, Shah V, Hirsch JA. Handb Clin Neurol. 2021;176:379–394. - PubMed
-
- Percutaneous vertebroplasty: a minimally invasive procedure for the management of vertebral compression fractures. Faiella E, Pacella G, Altomare C, et al. Osteology. 2022;2:139–151.
-
- Position statement on percutaneous vertebral augmentation: a consensus statement developed by the Society of Interventional Radiology (SIR), American Association of Neurological Surgeons (AANS) and the Congress of Neurological Surgeons (CNS), American College of Radiology (ACR), American Society of Neuroradiology (ASNR), American Society of Spine Radiology (ASSR), Canadian Interventional Radiology Association (CIRA), and the Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery (SNIS) Barr JD, Jensen ME, Hirsch JA, et al. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014;25:171–181. - PubMed
-
- Interventional radiology management of a ruptured lumbar artery pseudoaneurysm after cryoablation and vertebroplasty of a lumbar metastasis. Giordano AV, Arrigoni F, Bruno F, et al. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2017;40:776–779. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
