Bridging the molecular and clinical aspects of resveratrol in Alzheimer's disease: a review
- PMID: 40777747
- PMCID: PMC12328867
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-025-04451-x
Bridging the molecular and clinical aspects of resveratrol in Alzheimer's disease: a review
Abstract
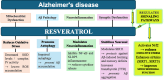
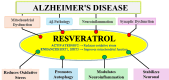
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive brain disorder that affects neurological functioning specifically targeting cognition, memory and behaviour. Pathology starts with the accumulation of tau proteins which on phosphorylation can be destructive for brain function. With gold standard drugs like Donepezil, there have been several attempts made to discover adjuvant therapeutic molecules such as plant-based products that could not only ease the ill-toward effects of these drugs, but also lead to the betterment of the patients suffering from AD. These are crucial in the management of patients of AD, by associations with psychological vulnerabilities and the overall loss of health of such individuals 'Resveratrol' is one such plant-based molecule which is a stilbene polyphenol present in many of the commonly occurring plants. Resveratrol is reported to have anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory properties which brings about the neuroprotection. Several studies have also been conducted that targets the signalling cascades involved during the progression of AD. This review attempts to give a collective information of its properties, its synthesis, metabolism and mechanisms that could drive researchers forward for its therapeutic applications during the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Anti-inflammatory; Anti-oxidant; Neurodegeneration; Neuroprotective; Resveratrol.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
References
-
- An L, Shen Y, Chopp M, Zacharek A, Venkat P, Chen Z, Li W, Qian Y, Landschoot-Ward J, Chen J (2021) Deficiency of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) exacerbates brain damage and cognitive deficit in a mouse model of vascular dementia. Aging Dis 12(3):732–746. 10.14336/AD.2020.0523 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources