Loss of intraflagellar transport 140 in osteoblasts cripples bone fracture healing
- PMID: 40777780
- PMCID: PMC12327822
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fmre.2022.09.006
Loss of intraflagellar transport 140 in osteoblasts cripples bone fracture healing
Abstract
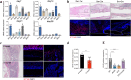
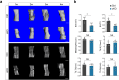
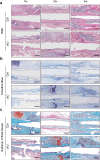
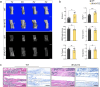
The indispensability of primary cilia in skeletal development has been widely recognized. We have previously shown that intraflagellar transport 140 (IFT140), a protein component of a bidirectional intraflagellar transport system required for ciliary function, controls bone development and dentinogenesis. However, it remains unknown whether IFT140 functionally contributes to bone fracture rehabilitation. Here an osteotomy-induced femoral fracture model was generated in Ift140-transgenic (Ift140-TG) and osteoblast-specific Ift140-conditional knockout (Ift140-cKO) mice. Micro-computed tomography, osteogenic induction, qualitative polymerase chain reaction, and toluidine blue and safranin O/fast green staining assays were used to characterize the dynamics of bone fracture healing from various perspectives. We found that IFT140 was relatively enriched in the bone callus and decreased in fracture-susceptible aged, or diabetic bones. Ift140-cKO mice had impaired osteogenic differentiation from bone mesenchymal stem cells, lower bone mass, and delayed fracture closure, whereas Ift140-TG mice had promising healing outcomes. Overall, our findings demonstrated for the first time that IFT140 has a beneficial role in fracture repair. Future investigation of the primary cilium in the context of aging and osteoporosis would certainly benefit patients at high risk of bone fractures.
Keywords: Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells; Bone fracture; Intraflagellar Transport 140; Osteoblasts; Primary Cilia.
© 2022 The Authors. Publishing Services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co. Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, raloxifene and teriparatide for the prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis.Health Technol Assess. 2005 Jun;9(22):1-160. doi: 10.3310/hta9220. Health Technol Assess. 2005. PMID: 15929857
-
Effectiveness and safety of vitamin D in relation to bone health.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007 Aug;(158):1-235. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007. PMID: 18088161 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of strontium ranelate for the prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal women.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Feb;11(4):1-134. doi: 10.3310/hta11040. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17280622
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cauley J.A., Giangregorio L. Physical activity and skeletal health in adults. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020;8:150–162. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

