CIRCumcision learning experience using simulation: A pilot learning platform for safe neonatal circumcision training offered either virtually or in person
- PMID: 40778046
- PMCID: PMC12327285
- DOI: 10.3389/fruro.2023.1199194
CIRCumcision learning experience using simulation: A pilot learning platform for safe neonatal circumcision training offered either virtually or in person
Abstract
Background: To our knowledge, no formal training combining didactic learning, simulation, and hands-on performance is available for practitioners performing neonatal circumcision. The absence of structured training may result in avoidable complications such as bleeding and penile injury. Herein, we present the results of a pilot neonatal circumcision training platform, offered either virtually or in person.
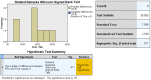
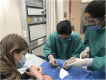
Material and methods: CIRCLES (CIRCumcision Learning Experience using Simulation) consist of 1. online didactic learning; 2. live simulation practice (in person or virtual coaching), and 3. clinical performance. Outcome measures included pre- and post-knowledge scores, self-efficacy questionnaires, and skill assessments of simulation and clinical performance (Likert rating). Face validity for training success was determined by an 80% passing score on the knowledge test and > 75% (mostly independent) performance.
Results: For this pilot, we restricted enrolment to seven pediatric residents and one nurse practitioner. Wilcoxon Sum Rank test for non-parametric paired samples for pre-and post-knowledge tests showed a median increase of 20 points in post-knowledge tests (p=0.011). Upon completion of the simulation training, all participants (8/8) have chosen to perform circumcision with the GOMCO clamp. Both in-person (4/4) and virtual participants (4/4) performed >75% of simulation and clinical circumcision independently. Post-training self-efficacy Z scores were higher than pre-training scores, except for the management of bleeding.
Conclusion: The pilot CIRCLES learning shows face validity for both in-person and virtual training for neonatal circumcision. We plan to extend this platform to include more trainees and to offer them to established practitioners. The availability of formal training may ultimately reduce adverse outcomes.
Keywords: circumcision training; education; neonatal circumcision; newborn; safe; virtual learning.
Copyright © 2023 Dos Santos, Alsabban, Maizels, Chua, Vuppal, Louca, Perlmutar, Knabl, Rickard, Varghese, Lorenzo and Koyle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors MK, AL, MR declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

