Tailored Tissue Plasminogen Factor Injection via Subdural Catheter for Subacute Subdural Hematoma in an Elderly Patient: A Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 40778251
- PMCID: PMC12325889
- DOI: 10.13004/kjnt.2025.21.e25
Tailored Tissue Plasminogen Factor Injection via Subdural Catheter for Subacute Subdural Hematoma in an Elderly Patient: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
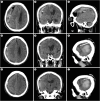
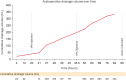
This report presents an 89-year-old patient with subacute subdural hematoma (SDH) treated with local anesthesia via burr-hole trephination (BHT) and subdural drain placement, followed by liquefaction of the hematoma using the fibrinolytic agent, tissue plasminogen activator (tPA). Initially, the patient presented with acute post-trauma SDH without neurological symptoms, for which conservative treatment was administered. About a week later, the patient developed hemiplegia and progressed to a stuporous state. Radiographic evidence indicated that the subacute SDH had evolved into a chronic stage with an increased mass effect, causing new neurological deficits. Although craniotomy was considered, general anesthesia was not performed at the caregiver's request. After BHT, a subdural catheter was placed, but initial drainage was minimal. tPA was then administered to promote liquefaction and drainage. Follow-up computed tomography of the brain confirmed significant drainage of the hematoma. The patient subsequently recovered consciousness and motor function. This report discusses a less-invasive alternative for managing symptomatic subacute SDH. My approach of combining BHT with fibrinolytic therapy using tPA facilitated effective evacuation of the hematoma with minimal surgical intervention. Here, I present a case where tPA was used, detailing the methodology, imaging findings, and clinical outcomes of fibrinolytic therapy.
Keywords: Catheterization; Hematoma, subdural, acute; Subdural space; Tissue plasminogen activator.
Copyright © 2025 Korean Neurotraumatology Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The author has no financial conflicts of interest. Informed Consent This study had Institutional Review Board approval, and the need to obtain informed patient consent was waived. Ethics Approval The study received an exemption from the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Soonchunhyang University Hospital Seoul (IRB No. 2024-10-022).
Figures

References
-
- Bullock MR, Chesnut R, Ghajar J, Gordon D, Hartl R, Newell DW, et al. Surgical management of acute subdural hematomas. Neurosurgery. 2006;58:S16–S24. - PubMed
-
- Frenkel MB, Sarwal A, Wren MP, Newey CR, Couture DE. Subdural instillation of a thrombolytic agent for treatment of recurrent subdural hematoma. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2017;40:279–280. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

