GLP-1R as a potential link between diabetes and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 40778306
- PMCID: PMC12328308
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1601602
GLP-1R as a potential link between diabetes and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
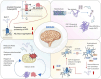
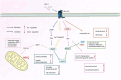
There is growing interest in the relationship between Alzheimer's disease (AD) and diabetes mellitus (DM), and the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) may be an important link between these two diseases. The role of GLP-1R in DM is principally to regulate glycemic control by stimulating insulin secretion, inhibiting glucagon secretion, and improving insulin signaling, thereby reducing blood glucose levels. In AD, GLP-1R attenuates the pathological features of AD through mechanisms such as anti-inflammatory effects, the reduction in amyloid-beta (Aβ) deposition, the promotion of Aβ clearance, and improvements in insulin signaling. Notably, AD and DM share numerous pathophysiological mechanisms, most notably the disruption of insulin signaling pathways in the brain. These findings further underscore the notion that GLP-1R plays pivotal roles in both diseases. Taken together, these findings lead us to conclude that GLP-1R not only plays an important role in the treatment of DM and AD but also may serve as a bridge between these two diseases. Future research should focus on elucidating the detailed molecular mechanisms underlying the actions of GLP-1R in both diseases and exploring the development of GLP-1R agonists with dual therapeutic benefits for AD and DM. This could pave the way for innovative integrated treatment strategies to improve outcomes for patients affected by these intertwined conditions.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; diabetes mellitus; glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; insulin resistance; neuroinflammation.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Huang, Wang, Huang, Shi, Luo and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preexisting Diabetes and Pregnancy: An Endocrine Society and European Society of Endocrinology Joint Clinical Practice Guideline.Eur J Endocrinol. 2025 Jun 30;193(1):G1-G48. doi: 10.1093/ejendo/lvaf116. Eur J Endocrinol. 2025. PMID: 40652450
-
Prognostic impact of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP1R) expression on cancer survival and its implications for GLP-1R agonist therapy: an integrative analysis across multiple tumor types.Geroscience. 2025 Jun;47(3):4413-4427. doi: 10.1007/s11357-024-01494-5. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 39777709 Free PMC article.
-
Mazdutide, a dual agonist targeting GLP-1R and GCGR, mitigates diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction: mechanistic insights from multi-omics analysis.EBioMedicine. 2025 Jul;117:105791. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105791. Epub 2025 Jun 6. EBioMedicine. 2025. PMID: 40479843 Free PMC article.
-
The evolution of type 2 diabetes management: glycemic control and beyond with SGLT-2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists.J Osteopath Med. 2023 Nov 3;124(3):127-135. doi: 10.1515/jom-2023-0179. eCollection 2024 Mar 1. J Osteopath Med. 2023. PMID: 37921061 Review.
References
-
- Barone E., Di Domenico F., Perluigi M., Butterfield D. A. (2021). The interplay among oxidative stress, brain insulin resistance and AMPK dysfunction contribute to neurodegeneration in type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 176 16–33. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.09.006 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Batista A. F., Forny-Germano L., Clarke J. R., Lyra E. S. N. M., Brito-Moreira J., Boehnke S. E., et al. (2018). The diabetes drug liraglutide reverses cognitive impairment in mice and attenuates insulin receptor and synaptic pathology in a non-human primate model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Pathol. 245 85–100. 10.1002/path.5056 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

