Artificial intelligence in personalized rehabilitation: current applications and a SWOT analysis
- PMID: 40778384
- PMCID: PMC12328449
- DOI: 10.3389/fdgth.2025.1606088
Artificial intelligence in personalized rehabilitation: current applications and a SWOT analysis
Abstract
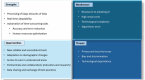
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming personalized rehabilitation by introducing innovative methods to enhance care across diverse medical specialties. Despite its potential, widespread implementation remains limited, largely due to a lack of comprehensive analyses on its benefits and barriers. This mini narrative review examines current applications of AI in personalized rehabilitation and provide a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis AI is already being used to develop personalized treatment plans, support ongoing patient management, and adapt therapy sessions in real-time. One of its key strengths is the capacity to process vast datasets and monitor real-time information, thereby elevating the level of personalization. Automation of certain tasks can reduce human error and alleviate clinician workload, allowing more time for direct patient care. Opportunities for AI lie in leveraging rapidly advancing technologies to meet the rising demand for rehabilitation services, particularly with aging populations. Collaborations with industry can accelerate innovation, while data sharing can promote best practices across institutions. However, notable challenges persist. High implementation costs, ethical concerns such as algorithmic bias, and risks of increasing healthcare disparities remain major barriers. Additionally, threats such as data privacy breaches and security vulnerabilities emphasize the need for robust, balanced regulatory frameworks. In conclusion, AI holds immense promise for transforming personalized rehabilitation. While current applications are largely in early stages or proof-of-concept phases, ongoing research, ethical foresight, and strategic collaboration are essential to maximize benefits and minimize risks for optimal patient outcomes.
Keywords: SWOT; artificial intelligence; healthcare; patient-centered approach; personalization; rehabilitation.
© 2025 Attoh-Mensah, Boujut, Desmons and Perrochon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

