Combinative Protein Expression of Immediate Early Genes c-Fos, Arc, and Npas4 Along Aversive and Appetitive Experience-Related Neural Networks
- PMID: 40778693
- PMCID: PMC12333481
- DOI: 10.1002/hipo.70030
Combinative Protein Expression of Immediate Early Genes c-Fos, Arc, and Npas4 Along Aversive and Appetitive Experience-Related Neural Networks
Abstract
Expression of immediate early genes (IEGs) is critical for memory formation and has been widely used to identify the neural substrate of memory traces, termed memory engram cells. Functions of IEGs have been known to be different depending on their types. However, there is limited knowledge about the extent to which different types of IEGs are selectively or concurrently involved in the formation of memory engram. To address this question, we investigated the combinative expression of c-Fos, Arc, and Npas4 proteins using immunohistochemistry following aversive and rewarding experiences across subregions in the prefrontal cortex (PFC), basolateral amygdala (BLA), hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG), and retrosplenial cortex (RSC). Using an automated cell detection algorithm, we found that expression patterns of c-Fos, Npas4, and Arc varied across different brain areas, with a higher increase of IEG expressing cells in the PFC and posterior BLA than in the DG. The combinative expression patterns, along with their experience-induced changes, also differed across brain areas; the co-expression of IEGs increased in the PFC and BLA following experience, whereas the increase was less pronounced in the DG and RSC. Furthermore, we demonstrate that different area-to-area functional connectivity networks were extracted by different IEGs. These findings provide insights into how different IEGs and their combinations identify engram cells, which will contribute to a deeper understanding of the functional significance of IEG-tagged memory engram cells.
Keywords: context conditioning; co‐expression; immediate early genes; immunohistochemistry; memory engram cell.
© 2025 The Author(s). Hippocampus published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

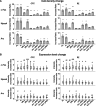

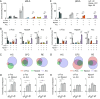
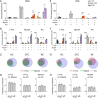

Update of
-
Combinative protein expression of immediate early genes c-Fos, Arc, and Npas4 along aversive- and reward-related neural networks.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 22:2025.04.21.649441. doi: 10.1101/2025.04.21.649441. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Hippocampus. 2025 Sep;35(5):e70030. doi: 10.1002/hipo.70030. PMID: 40475597 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Abraham, W. C. , Mason S. E., Demmer J., et al. 1993. “Correlations Between Immediate‐Early Gene Induction and the Persistence of Long‐Term Potentiation.” Neuroscience 56: 717–727. - PubMed
-
- Alexander, A. S. , and Nitz D. A.. 2015. “Retrosplenial Cortex Maps the Conjunction of Internal and External Spaces.” Nature Neuroscience 18: 1143–1151. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

