MRI-based radiomics for preoperative T-staging of rectal cancer: a retrospective analysis
- PMID: 40778975
- PMCID: PMC12334464
- DOI: 10.1007/s00384-025-04969-9
MRI-based radiomics for preoperative T-staging of rectal cancer: a retrospective analysis
Abstract
Puropose: Preoperative T-staging in rectal cancer is essential for treatment planning, yet conventional MRI shows limited accuracy (~ 60-78). Our study investigates whether radiomic analysis of high-resolution T2-weighted MRI can non-invasively improve staging accuracy through a retrospective evaluation in a real-world surgical cohort.
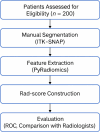
Methods: This single-center retrospective study included 200 patients (January 2024-April 2025) with pathologically confirmed rectal cancer, all undergoing preoperative high-resolution T2-weighted MRI within one week prior to curative surgery and no neoadjuvant therapy. Manual segmentation was performed using ITK‑SNAP, followed by extraction of 107 radiomic features via PyRadiomics. Feature selection employed mRMR and LASSO logistic regression, culminating in a Rad-score predictive model. Statistical performance was evaluated using ROC curves (AUC), accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and Delong's test.
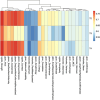
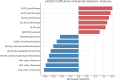
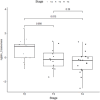
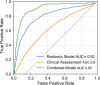
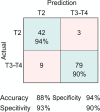
Results: Among 200 patients, 95 were pathologically staged as T2 and 105 as T3-T4 (55 T3, 50 T4). After preprocessing, 26 radiomic features were retained; key features including ngtdm_contrast and ngtdm_coarseness showed AUC values > 0.70. The LASSO-based model achieved an AUC of 0.82 (95% CI: 0.75-0.89), with overall accuracy of 81%, sensitivity of 78%, and specificity of 84%.
Conclusion: Radiomic analysis of standard preoperative T2-weighted MRI provides a reliable, non-invasive method to predict rectal cancer T-stage. This approach has the potential to enhance staging accuracy and inform personalized surgical planning. Prospective multicenter validation is required for broader clinical implementation.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence; MRI; Oncologic Imaging; Radiomics; Rectal cancer.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval: This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Review Committee of the University Hospital of Campania "L. Vanvitelli" and AORN "Ospedale dei Colli" in Naples (Protocol No. 13953/i/2022). Informed consent: An exemption from the requirement for patient informed consent was granted by the ethics committee due to the retrospective nature of the study. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Haga A et al (2019) Standardization of imaging features for radiomics analysis. J Med Invest 66(12):35–37 - PubMed
-
- Yushkevich PA et al (2006) User-guided 3d active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage 31(3):1116–1128 - PubMed
-
- Shu Z et al (2022) Multiparameter MRI-based radiomics for preoperative prediction of extramural venous invasion in rectal cancer. Eur Radiol 32(2):1002–1013 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

