Comprehensive Mendelian randomization analysis of inflammatory networks in diabetic nephropathy and pituitary adenoma: unveiling complex causal relationships
- PMID: 40779076
- PMCID: PMC12334379
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-03291-8
Comprehensive Mendelian randomization analysis of inflammatory networks in diabetic nephropathy and pituitary adenoma: unveiling complex causal relationships
Abstract
Background: The intricate relationships between inflammatory pathways, diabetic nephropathy, and pituitary adenomas remain poorly understood. This study aimed to comprehensively investigate the causal associations between inflammatory factors, diabetic nephropathy, and pituitary adenoma risk using Mendelian randomization approaches.
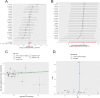
Methods: We conducted a systematic Mendelian randomization analysis employing multiple statistical methods including inverse variance weighted (IVW), MR-Egger, and weighted mode approaches. A comprehensive inflammatory factor profile encompassing cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, and immunoregulatory molecules was analyzed. Sensitivity analyses including scatter plots and funnel plots were performed to validate the robustness of causal inferences.
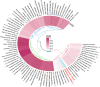
Results: The panoramic analysis revealed distinct inflammatory signatures associated with disease risk. For pituitary adenomas, Neurotrophin-3 demonstrated significant protective effects (OR = 0.754, 95% CI: 0.583-0.975, P = 0.031), while programmed cell death 1 ligand emerged as a risk factor (OR = 1.320, 95% CI: 1.016-1.714, P = 0.037). Regarding diabetic nephropathy, six inflammatory factors showed significant associations: CX3C-motif chemokine 1 (OR = 0.514, P = 0.049), interleukin-13 (OR = 0.822, P = 0.014), TNF-beta (OR = 0.903, P = 0.011), and TNF-related activation-induced cytokine (OR = 0.905, P = 0.037) exhibited protective effects, whereas macrophage colony-stimulating factor (OR = 1.175, P = 0.026) and matrix metalloproteinase-10 (OR = 1.142, P = 0.030) increased disease risk. Notably, no significant causal relationship was observed between diabetic nephropathy and pituitary adenoma risk across all analytical methods.
Conclusions: This comprehensive Mendelian randomization analysis reveals complex, disease-specific inflammatory networks underlying diabetic nephropathy and pituitary adenoma pathogenesis.
Keywords: Causal inference; Diabetic nephropathy; Inflammatory factors; Mendelian randomization; Pituitary adenoma.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not available. Consent for publication: Not available. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Kou J, Wei T, Liu H, Sun L, Ding D, Song S. Temporal trends in cross-country inequalities of chronic kidney disease attributable to temperature exposure from 1990 to 2021. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. - PubMed
-
- Ansari Z, Chaurasia A, Neha, Sharma N, Bachheti RK, Gupta PC. Exploring inflammatory and fibrotic mechanisms driving diabetic nephropathy progression. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2025. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
