Recent Advances in Regulation Strategy and Catalytic Mechanism of Bi-Based Catalysts for CO2 Reduction Reaction
- PMID: 40779212
- PMCID: PMC12334405
- DOI: 10.1007/s40820-025-01860-8
Recent Advances in Regulation Strategy and Catalytic Mechanism of Bi-Based Catalysts for CO2 Reduction Reaction
Abstract
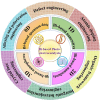
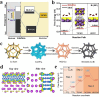
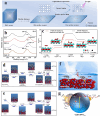
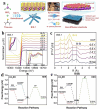
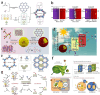
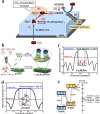
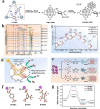
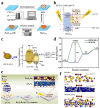
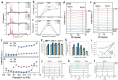
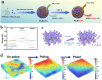
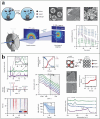
Using photoelectrocatalytic CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR) to produce valuable fuels is a fascinating way to alleviate environmental issues and energy crises. Bismuth-based (Bi-based) catalysts have attracted widespread attention for CO2RR due to their high catalytic activity, selectivity, excellent stability, and low cost. However, they still need to be further improved to meet the needs of industrial applications. This review article comprehensively summarizes the recent advances in regulation strategies of Bi-based catalysts and can be divided into six categories: (1) defect engineering, (2) atomic doping engineering, (3) organic framework engineering, (4) inorganic heterojunction engineering, (5) crystal face engineering, and (6) alloying and polarization engineering. Meanwhile, the corresponding catalytic mechanisms of each regulation strategy will also be discussed in detail, aiming to enable researchers to understand the structure-property relationship of the improved Bi-based catalysts fundamentally. Finally, the challenges and future opportunities of the Bi-based catalysts in the photoelectrocatalytic CO2RR application field will also be featured from the perspectives of the (1) combination or synergy of multiple regulatory strategies, (2) revealing formation mechanism and realizing controllable synthesis, and (3) in situ multiscale investigation of activation pathways and uncovering the catalytic mechanisms. On the one hand, through the comparative analysis and mechanism explanation of the six major regulatory strategies, a multidimensional knowledge framework of the structure-activity relationship of Bi-based catalysts can be constructed for researchers, which not only deepens the atomic-level understanding of catalytic active sites, charge transport paths, and the adsorption behavior of intermediate products, but also provides theoretical guiding principles for the controllable design of new catalysts; on the other hand, the promising collaborative regulation strategies, controllable synthetic paths, and the in situ multiscale characterization techniques presented in this work provides a paradigm reference for shortening the research and development cycle of high-performance catalysts, conducive to facilitating the transition of photoelectrocatalytic CO2RR technology from the laboratory routes to industrial application.
Keywords: Bismuth-based catalysts; CO2 reduction reaction; Catalytic mechanism; Regulation strategy; Review.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicting interests. They have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. All authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures










References
-
- X. Li, S. Wang, L. Li, Y. Sun, Y. Xie, Progress and perspective for in situ studies of CO2 reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142(21), 9567–9581 (2020). 10.1021/jacs.0c02973 - PubMed
-
- J. Fu, K. Jiang, X. Qiu, J. Yu, M. Liu, Product selectivity of photocatalytic CO2 reduction reactions. Mater. Today 32, 222–243 (2020). 10.1016/j.mattod.2019.06.009
-
- X. Li, W. Bi, M. Chen, Y. Sun, H. Ju et al., Exclusive Ni-N4 sites realize near-unity CO selectivity for electrochemical CO2 reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139(42), 14889–14892 (2017). 10.1021/jacs.7b09074 - PubMed
-
- X. Shen, Q. Meng, M. Dong, J. Xiang, S. Li et al., Low-temperature reverse water–gas shift process and transformation of renewable carbon resources to value-added chemicals. Chemsuschem 12(23), 5149–5156 (2019). 10.1002/cssc.201902404 - PubMed
-
- D. Cui, W. Hao, J. Chen, The synergistic effect of heteroatom doping and vacancy on the reduction of CO2 by photocatalysts. ChemNanoMat 7(8), 894–901 (2021). 10.1002/cnma.202100148
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
