Surveillance of single nucleotide polymorphisms correlated to macrocyclic lactone resistance in Dirofilaria immitis from client-owned dogs across the United States
- PMID: 40779992
- PMCID: PMC12355919
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2025.100604
Surveillance of single nucleotide polymorphisms correlated to macrocyclic lactone resistance in Dirofilaria immitis from client-owned dogs across the United States
Abstract
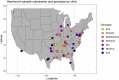
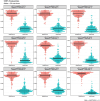
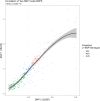
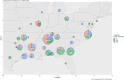
Dirofilaria immitis is a parasitic filarial nematode and the causative agent of heartworm disease in canids and other species. Heartworm disease is predominantly managed via macrocyclic lactone (ML) - based chemoprophylactics. Through opportunistic sampling, genotypically and phenotypically confirmed ML-resistant D. immitis isolates have been isolated in the Lower Mississippi River Valley region (LMRV); however, the pervasiveness of resistant isolates in the USA has not been evaluated. This study aimed to evaluate the geographic distribution and prevalence of genotypically ML-resistant heartworms in client-owned dogs across the USA over a 3-year period. Owner consent was obtained to collect microfilaremic blood samples from heartworm-positive dogs from participating clinics. Veterinarians completed a questionnaire on the known history of each dog, including treatment and travel history. A total of 310 microfilaremic blood samples were collected from 45 geographically diverse veterinary clinics located in 22 states. Microfilariae were filtered from blood, DNA extracted utilizing the QIAGEN QIAamp DNA Micro Kit and samples sequenced by the Génome Québec Innovation Centre to determine allele frequencies at nine SNP sites previously correlated with ML resistance. The highly predictive 2-SNP model was used to identify genotypically susceptible, mixed, and resistant populations. Computational analysis indicated 111 (35.8 %) were genotypically susceptible, 96 (31.0 %) were genotypically resistant, and 103 (33.2 %) were genotypically mixed. The genotypically mixed and ML-resistant infections were located within and outside of the endemic LMRV, as far north as Michigan, which indicates canine populations outside of the LMRV are at increased risk for transmission of potentially ML-resistant heartworm infections than previously hypothesized. Veterinary practitioners across the USA need to be aware of the potential risks of ML resistance heartworm infections and ensure patient compliance with recommended prevention protocols.
Keywords: Drug resistance; Genotype; Heartworms; Macrocyclic lactones; Molecular markers; Surveillance.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:Emily Curry, David Tack, Jessica Rodriguez, Danielle Brehm-Lowe, John Letherer, Megan Lineberry and Tobias Clark reports a relationship with Zoetis Inc. that includes: employment. Roger Prichard received financial support for the genotype analysis from Zoetis Inc.
Figures
References
-
- AHS Heartworm incidence maps. 2022. https://www.heartwormsociety.org/veterinary-resources/incidence-maps
-
- Blagburn B.L., Dillon A.R., Arther R.G., Butler J.M., Newton J.C. Comparative efficacy of four commercially available heartworm preventive products against the MP3 laboratory strain of Dirofilaria immitis. Vet. Parasitol. 2011;176:189–194. - PubMed
-
- Bourguinat C., Keller K., Bhan A., Peregrine A., Geary T., Prichard R. Macrocyclic lactone resistance in Dirofilaria immitis. Vet. Parasitol. 2011;181:388–392. - PubMed
-
- Bourguinat C., Keller K., Prichard R.K., Geary T.G. Genetic polymorphism in Dirofilaria immitis. Vet. Parasitol. 2011;176:368–373. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

