Patient perceptions of outcomes used to evaluate in-hospital handover interventions: a rapid review of qualitative data
- PMID: 40780712
- PMCID: PMC12336611
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2025-100883
Patient perceptions of outcomes used to evaluate in-hospital handover interventions: a rapid review of qualitative data
Abstract
Objectives: High quality handover is critical for patient safety and care continuity. Existing practice is based on a weak evidence base in which the patient voice is poorly captured. The aim of this study was to identify outcomes of importance to patients, families and carers regarding interventions to improve in-hospital handover between healthcare practitioners.
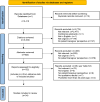
Design: A rapid systematic review of qualitative literature was carried out after prospective registration with PROSPERO and was reported in accordance with Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses and Enhancing Transparency in Reporting the Synthesis of Qualitative Research guidelines.
Data sources: The Ovid MEDLINE database was searched.
Eligibility criteria: Qualitative or mixed-methods studies reporting patient, family or caregiver perspectives on in-hospital handovers were eligible for inclusion.
Data extraction and synthesis: Synthesis was informed by the best-fit framework approach using a published taxonomy of handover-related outcomes and the Core Outcome Measures in Effectiveness Trials taxonomy. Outcomes were reported according to two distinct types of handover: bedside (patient-involved) and provider-focused (patient-uninvolved).
Results: A total of 34 studies, including 1262 participants across a range of specialties and predominantly high-income settings, were analysed. 53 bedside and 31 provider-focused handover outcomes were identified according to four domains; adverse events, quality of patient care, quality of handover and patient/caregiver satisfaction. Bedside handover studies frequently reported outcomes relating to patient engagement and communication with healthcare staff. One study was carried out in a low income country; however, outcomes identified were broadly similar.
Conclusions: These findings expand the known outcomes for evaluating handover interventions and highlight the importance of prioritising the patient and public perspective in research. This work will contribute to developing a core outcome set for trials in surgical handover but can also be applied to handover practices for any other discipline within the hospital environment.
Prospero registration number: CRD42023493367.
Keywords: Methods; Patient Participation; Patient Reported Outcome Measures; Patient Satisfaction; QUALITATIVE RESEARCH; STATISTICS & RESEARCH METHODS.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for interpersonal communication about end of life care between health practitioners and affected people.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 8;7(7):CD013116. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013116.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35802350 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Eliciting adverse effects data from participants in clinical trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 16;1(1):MR000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000039.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29372930 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources